SEO for AI Search in 2026: Technical & Content Strategies That Actually Work

How to find pages ignored by GoogleBot
Before indexing a page, search engines must make at least one visit to that page. For JavaScript sites, the number of visits before indexing will be at least 2 times. Accordingly, you need to monitor the pages ignored by GoogleBot to understand which of your pages will not be indexed.
Why is it important to monitor pages that are not visited by search engines?
We recommend auditing pages ignored by GoogleBot regularly. It helps to find some problems, for example, to check if crawlers can find new pages.
If search engines do not visit a certain page for several months, the page will likely be dropped from the index.
If the search robot visits the pages very rarely, then the bot does not see content updates. Accordingly, the SERP may contain outdated snippets or outdated information.
Step-by-step instruction for analyzing pages ignored by GoogleBot
This analysis is available to users who have integrated search engine logs.
Go to the “Logs” menu – the “Impact” report.
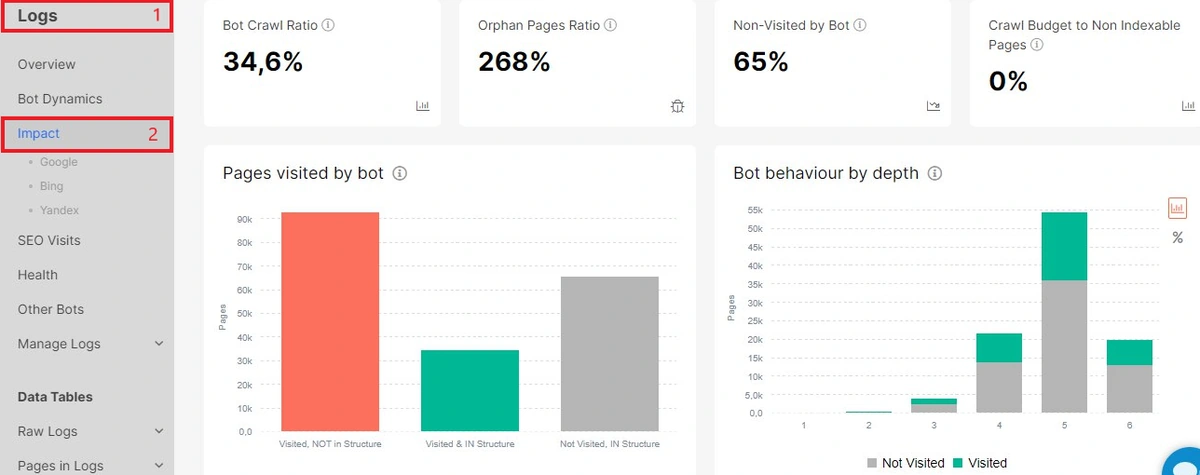
Next, go to the “Pages visited by bot” chart. Here you will see the ratio of pages visited and ignored by the search engine. Perfect when you have all the pages “Visited and in the structure”.
Click on the “NOT Visited, In structure” column to go to the data table with a list of pages ignored by GoogleBot.
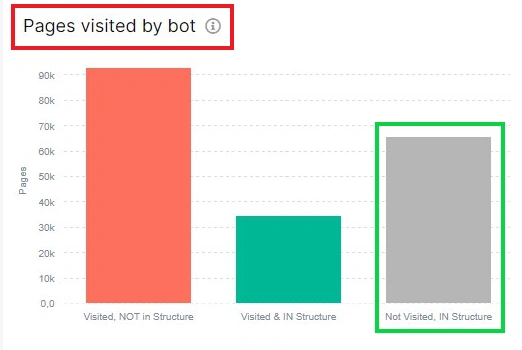
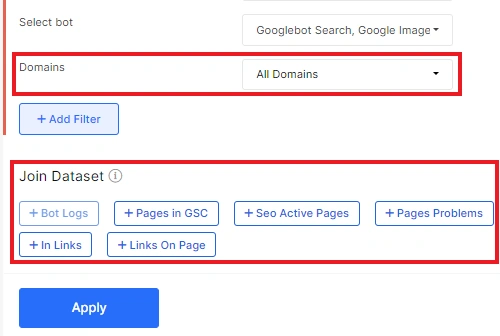
On this page, you can configure the dataset. Choose the period for which you want to see the pages ignored by the bot.
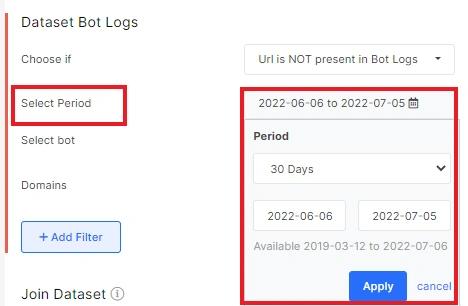
You can also choose a search robot. For example, you can see pages ignored by all search engines, AdWords bot, GoogleBot Images or GoogleBot Mobile, etc.
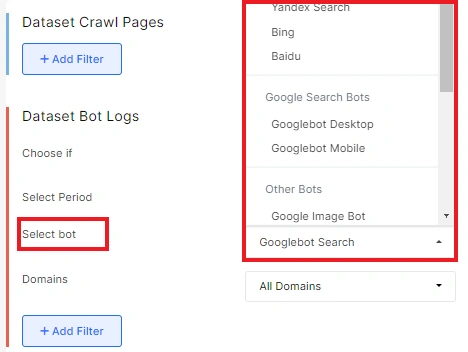
Select the desired domain or analyze all domains. You can also add any other filters or join datasets.
In the finished table, you will see a list of all URLs that the search robot did not visit during the period you selected. Note that this list contains only those URLs that were found in the crawl results.
You can export the dataset in a convenient format, save the selected URLs as a separate segment, create a KPI or save them as a problem.
Why search engines aren’t visiting pages on your website
Possible reasons why crawlers are not visiting certain pages:
- there are no entry links for the search robot (the pages are not in the sitemaps and they are not found in the code of the pages inside <a href=>);
- poor internal linking (search engines consider the page unimportant because of this);
- overly complicated or unclear site structure;
- pages are blocked for search robots crawling, for example, by the robots.txt file.
Once you find the reason why the search robot is ignoring your pages, it is recommended to fix the problem so that these pages are indexed in the future.


