SEO for AI Search in 2026: Technical & Content Strategies That Actually Work

Indexing without surprises: key aspects to avoid unexpected indexation challenges
Every SEO specialist has encountered unexpected indexing issues at least once. In this article, we will discuss the main aspects that need to be carefully monitored to prevent surprises with indexing.
Changes in the robots.txt file
Modifying the robots.txt file, even in a minor way, can inadvertently lead to search engines will be banned from the crawling of your website pages. This has been experienced by our clients on multiple occasions, particularly during releases when developers unintentionally added a ban on scanning the entire website through changes to the robots.txt file. The consequences were very fast, as the number of pages indexed by Google decreased significantly.
To prevent such incidents, it is crucial to have proactive discussions with developers and other specialists who have access to edit the robots.txt file. Set a clear protocol that ensures no changes can be made without obtaining your approval beforehand. By establishing this process, you can minimize the risks associated with inadvertent robots.txt modifications and maintain uninterrupted crawling and indexing of your website pages.
Availability of the robots.txt file
If the robots.txt file is not accessible and returns a 5xx status code, Google may assume that your website is completely prohibited from being crawled. It is crucial to monitor the availability of the robots.txt file meticulously to prevent such situations.
To avoid this issue, we recommend setting up alerts in your logs. Here’s how you can do it:
- go to the “Alerts” section of your website management platform;
- select “Logs Alerts” to configure alerts specifically for log data;
- сreate a new alert with the following settings.
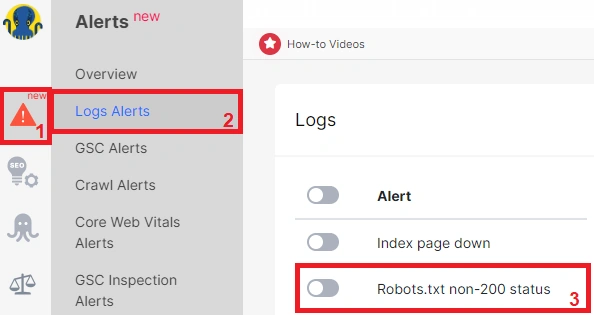
Configure conditions: сhoose “URL” and set “URL Path =” – “robots.txt”. Add an additional condition by selecting “Status Code” and set it to “Not equal” – “200”.
Alert configuration: іet “Rows count” – “Current count” and choose “> Greater than” with a value of “0”.
By configuring the alert this way, you will receive a notification if the Googlebot encounters a non-200 status code while accessing the robots.txt file. If you receive such a notification, it is crucial to address the problem immediately by ensuring that the robots.txt file returns a 200 response code.
Indexation and canonical rules changes
In some instances, changes in canonicals or indexing rules can occur due to technical errors, leading to undesired consequences. It is crucial to continuously monitor these rules to ensure their accuracy and adherence. One effective way to stay informed about any potential issues is by setting up alerts in the “Crawl Alerts” section of your website management platform.
Here’s how you can do it:
- go to the “Crawl Alerts” section;
- configure relevant alerts to monitor changes in indexing rules and canonicals (there are such builtin alerts as “Canonicals URL Changed” and “Increase in Non Indexable pages”);
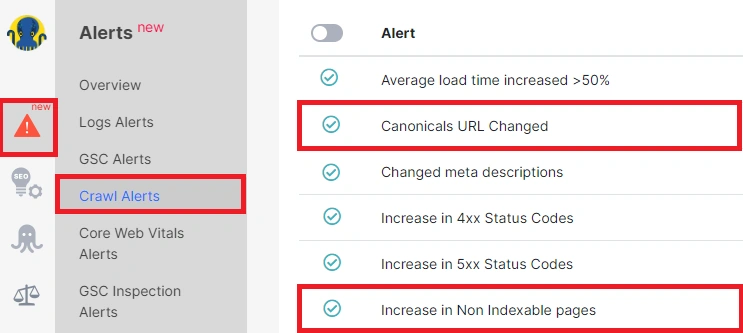
- create or edit the alert that suits your requirements, ensuring it covers the necessary conditions for detecting potential errors.
Once the alert is set up, you will receive notifications whenever changes or problems with indexing rules and canonicals are detected.
Googlebot is highly sensitive to changes in indexing and problems with canonicals. Therefore, if any such situations arise, it is crucial to promptly correct the errors to ensure proper indexing and ranking of your website pages.
Automatic generation of duplicate pages by your CMS
You may not even realize that your CMS is generating thousands of technical pages that are available for crawling and indexing. Therefore, it is worth regularly examining the logs of search bots to detect such technical pages. If there are such technical pages, the bot can spend the entire crawl budget on these pages, instead of scanning the pages you want to see in the SERP.
Infinite pagination
Infinite pagination poses another common problem. In this scenario, the last page of pagination contains a link to the next page, but the two pages are identical. For example, if you have a category page with 100 products and display 10 products per page, you logically expect 10 pages of pagination. However, on the tenth page, there might be a link to the eleventh page, which is a duplicate of the tenth. Regularly scanning your website and identifying complete duplicate pages is necessary to avoid this issue.
Broken URLs in XML sitemaps
Broken URLs in HTML sitemaps can consume your crawl budget, preventing bots from crawling and indexing indexable pages. To detect this problem, conduct a sitemap scan. Then review the crawl results and examine the “Sitemap” report, paying attention to non-200 status code pages. Remove these broken URLs from the sitemap to prevent unnecessary crawling.
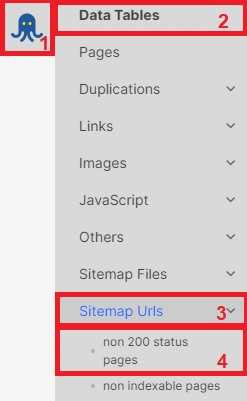
In cases where it is impractical to remove a large number of broken URLs from the sitemap, it may be advisable to abandon the sitemaps altogether to prevent wasting your crawl budget.
Redirects stop working
In general, if you had migrations or configured redirects for individual pages, you should always keep these redirects and not disable them. Because disabling redirects can lead to a sudden increase in 404 status codes on your website, negatively impacting both user experience and your crawl budget. It is vital to preserve these redirects to ensure a smooth user journey and efficient crawling and indexing by search engines.
***
By combining careful monitoring of all of these points, content, internal links, JavaScript, server-side rendering, and conducting regular audits, you can proactively manage your website’s indexing and ensure a seamless user experience. This proactive approach helps you stay ahead of any unexpected challenges and maintain a well-optimized website for both users and search engines.


