
401 response codes: a how-to for diagnosing and resolving log file issues
You may have noticed in the Google Search Console reports that some of your pages were not scanned and indexed by Googlebot due to the 401 (Unauthorized) status code. You could also pay attention to this status code by analyzing search engine logs. This is a common issue, so we have decided to share how to find a complete list of such pages and how to fix this problem.
What is a 401 (Unauthorized) status code?
A web server returns a 401 (Unauthorized) status code if the authentication credentials for access is required. In other words, the page is password-protected, and the content of the page becomes available only after entering these credentials. However, Googlebot does not have or use any login data.
Why is it important to check 401 pages in logs?
As mentioned before, pages with a 401 status code are not accessible to Google and will never be accessible, because Googlebot does not use any data for authorization. As a result, search bots cannot access the content of the page. Accordingly, the page cannot be indexed and users will not be able to google this information.
Another reason to prioritize the checking of 401 pages in logs is because it wastes crawl budget. Search engines tend to crawl pages that are useful and accessible, and if they encounter several pages with a 401 status code, it can result that indexable and crawlable pages may not be crawled and scanned.
So, if among the 401 pages there are those that contain important information and which you want to see in the SERP, you need to fix the 401 status code for these pages. It is also necessary to reduce the number of entry points for 401 pages, if part of the pages should really have an authorization for users.
How to find 401 pages in logs
As a powerful log analyzer, JetOctopus analyzes all pages and all response codes received by Googlebot and other search engines that visited your website. So you can find all 401 pages very easily.
To do this, go to the “Logs” section and select the “Bot Details” dashboard, as shown in the screenshot.
If you haven’t connected logs yet, it can be done in just a few minutes, and more information can be found in the article: Log file integration: everything you need to know.
Next, choose the period, bot, and domain for which you want to receive data, as shown in screenshot below.
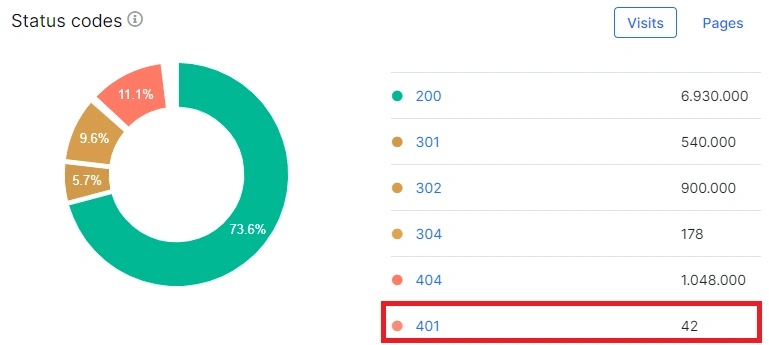
Then scroll down the dashboard and go to the “Status codes” chart, where you can see the distribution status of the codes received by your selected bot during the set period. If even one page returned a 401 (Unauthorized) response code, you’ll see it on the chart.
All chart segments and status codes are clickable, so you can click on the 401 status code to go to the data table with detailed data, which includes the exact URL, the time of the visit, the exact user agent, and more.
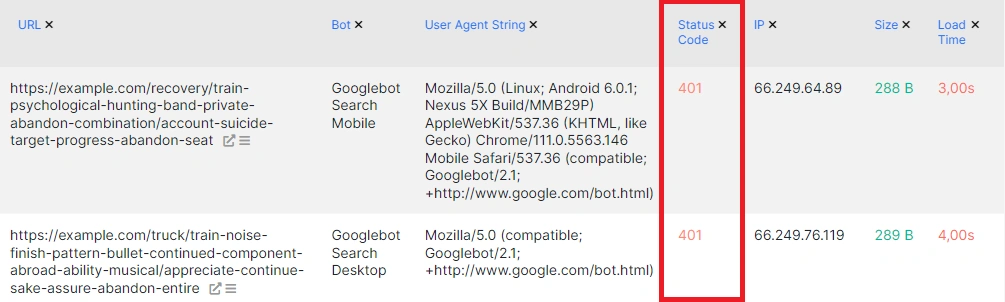
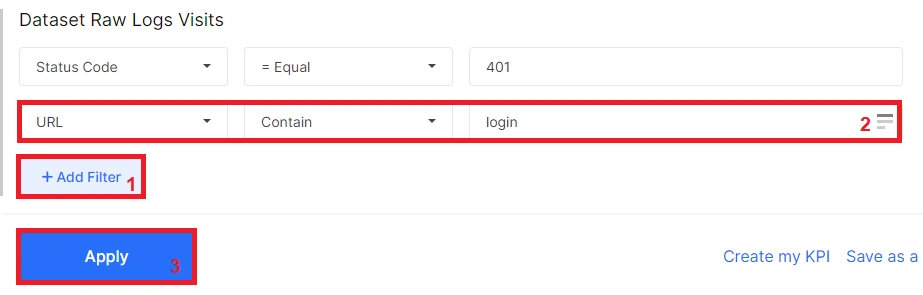
Additionally, you can filter pages by URL path, for example, by selecting only those pages that contain “login” in the URL, as shown in the screenshot.
How to fix 401 status codes
To determine whether you need to fix 401 pages for Googlebot, you must review all pages. It will be very convenient to use the functionality of segments to automate work.
- If you want a page to appear in the SERP, but users must log in to view it, you need to configure specific settings on the web server. Based on the reverse DNS lookup or by checking the user agent string and verified IP, the web server must return a 200 OK status code and the content of the page to bots. At the same time, the web server should return a 401 status code to users.
- If the page should not be in the SERP, prevent crawling of this page in the robots.txt file.
- If the page should not be crawled and indexed, but you cannot create a rule to prevent crawling in the robots.txt file (for example, if you have many pages with different links), we recommend removing the links from your website to these pages. To do this, you can turn these links into buttons that are not inside an <a href> element. Alternatively, these links can appear after the user performs an action on the webpage. This way, you will make the links unavailable to search engines, and users will be able to click and go to the desired page after logging in.
- Remove links to 410 pages in sitemaps.
In addition to 401, there may be other non 200 status codes in the logs. we recommend that you read the information about these status codes:
How to find blinking status codes in search robots logs
Step-by-step instructions: analysis of 404 URLs in search engine logs

