
How to manage redirect chains
In this article, we will guide you on what to do if you encounter redirect chains while scanning your website.
Redirect chains occur when a page redirects the client’s browser to another page, and then another, and then another.
The number of redirects in a chain can be quite large; if it is more than five, search engines might stop processing the redirect and not follow it to the end. If the number exceeds 10, then search engines will almost certainly not reach the final destination.
Similarly, if the number of redirects in the chain becomes substantial, the client’s browser may not fully load the redirect location page, resulting in a “too many redirects” error.
Detecting redirect chains on your website
After conducting a comprehensive website scan, follow these steps to identify redirect chains. Navigate to the “Technical” – “Statuses” dashboard and locate the “Redirect Chains” built-in data table.
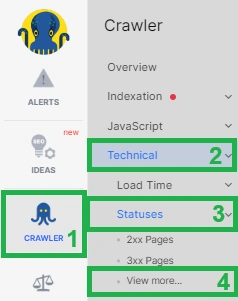
In this datatable, you’ll find pages that have experienced more than one redirect.
Example:
https://example.com/page=1 – 301 – https://example.com/page=2 – 301 – https://example.com/page=3 – 200 OK
How to address redirect chains?
Set up redirects for each URL within the chain, ensuring the final URL returns a 200 status code without intermediate redirects. If your chain has 3 redirects, establish a 301 redirect from the initial URL to the final URL (returning a 200 status code). Similarly, configure a direct 301 redirect from the second URL in the chain to the final URL (also returning a 200 status code).
Example:
https://example.com/page=1 – 301 – https://example.com/page=3 – 200 OK
https://example.com/page=2 – 301 – https://example.com/page=3 – 200 OK
Repeat this process for each link within the redirect chain.
Even after resolving the issues, it’s recommended to remove links pointing to redirect chains. To find them, go to the “Links” data table”.
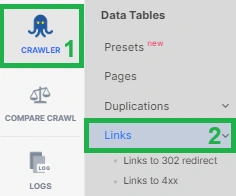
Add the “Link destination” dataset, then click the “+Add filter” button. Select the filter “[Destination page] Redirect Target Status Code” – “Between” “300 and 399.” Click “Apply.”
The resulting table will display links containing links to redirect chains. The “Page URL” column shows pages where links to redirect chains were found in the HTML code, and the “Link destination (absolute URL)” column provides links to the redirects themselves.
Lastly, it’s advisable to remove all links pointing to redirect chains from your sitemaps.
By taking these steps, you can efficiently identify and address redirect chains, optimizing your website’s performance and ensuring a smooth user experience.

