
How to use the “Query on Page” dataset for an SEO boost
The “Query on Page” dataset is one of the best tools that will help improve your website’s rankings in search results. By analyzing this data, you can delve into the analysis of real user queries and whether your website pages have relevant metadata, headings, etc. For example, users may search for “green pencil”, but you may not have this query in the needed HTML elements (as a result, in the snippet as well), so the CTR may be lower.
What data does the “Query on page” dataset contain
The “Query on Page” dataset combines data from two sources: Google Search Console and crawl results. That is, you will get real data from Google search and the latest information about HTML elements, such as title, meta description and H1, from crawling.
To analyze queries on a page, go to the desired crawl or start a new one. We recommend using data from new crawls, as the title or meta-data may have changed since the last crawl.
Next, go to the Google Search Console section – Data Tables – “Query on page”. Here you can find three separate datasets:
- “Query in title”;
- “Query in meta-description”
- “Query in H1”.
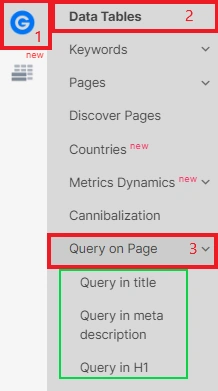
Next step, select the desired dataset. Adjust the period, country and device type. With these detailed settings, you can check how successful your SEO campaign is for different types of devices and countries.
We want to focus your attention on the fact that the dataset “Query on page” displays information only for those URLs found and scanned by JetOctopus during the corresponding crawl. If you want to get information about all URLs that are effective in search results, you can run a crawl of URLs from Google Search Console.
More information: How to use the list mode: 5 tips.
Query in title
The title is one of the most important elements that Google uses when ranking a page in SERP. Also, users see the title in the snippet and pay attention to it when choosing a URL to click on.
But the titles on our website do not always correspond to the search queries of real users. Therefore, we combined data from Google Search Console and crawl results to determine the pages that can be boosted by adding queries to the title.
In the “Query in Title” data table, you will see the following columns:
- “Queries” – data from the Google Search Console; the query for which the page had impressions in SERP;
- “Query in title ratio” – how much the query matches the word form in the title; for example, users search for “jetoctopus” and “jet octopus”, these are different word forms, but the pages are ranked the same for this query; the ratio for one will be 100%, for the other – 0%;
- “Title” – the title of the page from crawl results; we highlight queries in the title with color – it is very convenient to analyze queries; if the words are similar, but not 100% the same, we also highlight them; for example, the query contains “decaf coffee”, and in the title, we will highlight “decaffeinated coffee”, because they are similar words; search engines work the same way: they rank pages not only by a complete match between the query and the word in the title but also by words with a similar meaning;
- clicks and impressions are important metrics to analyze.
Query in meta description
The dataset “Query in meta description” is built according to the same principle as “Query in title”. The description has no direct impact on search engine ranking, but it does impact the clickability of the page. Because the meta description is displayed in the snippet and users get information about the page from it. If the meta description is not unique or does not contain the required information, the user may not click on the page.

Query in H1
The “Query in H1” dataset contains data on queries from the GSC in the H1 heading. Note the fact that we are analyzing the first H1. If you have two or more H1 headings on your page, we will not be able to display information for each H1.
Headings help search engines understand the main content of the page, so they must contain relevant queries.
How to analyze the “Queries on Page” dataset
Agree that “Queries on Page” is a great tool for analyzing the current state of your website, but also the tool that will allow you to quickly boost organic traffic. Below we will offer an effective scheme, but before that, we will tell you what to focus on when analyzing “Queries on Page”.
1. The number of impressions, clicks and CTR. Highlight the most effective and least effective pages for different queries. Maybe people often search for a query, your page is even ranked in the SERP, but there is not any click, because it is not clear from the snippet that the page contains needed information for the user.
2. Average position. Even if the title, meta description and H1 contain the desired query, but the position is low, it is a reason to think about internal and external optimization of the page.
3. Cannibalization. Yes, it is important to analyze such cases and understand whether they are not a problem for you.
More information: How to eliminate and fix cannibalisation issues.
4. Duplicate queries in the title, meta description and H1 – merge these data to understand how the number of clicks and impressions changes if several pages contain the same query. Pay attention to which additional queries the following pages are ranked for.
We recommend using the “Join Dataset” and “Segments” options for deeper analysis.
And now let’s talk about how to boost organic traffic quickly, using the results of the “Query on Page” analysis.
To begin, select the least clickable pages in positions 1-5. You can configure the necessary filters for the dataset by clicking on the “+Add filter” button.
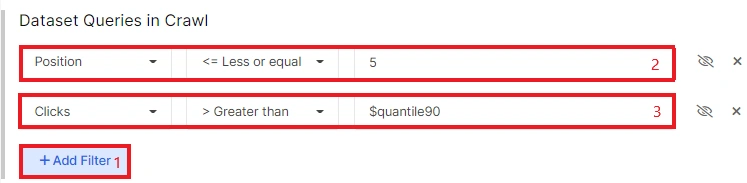
Add columns “Query in meta description”, “Query in title ratio”, “Title”, “Query in first H1 ratio”, “First H1”.
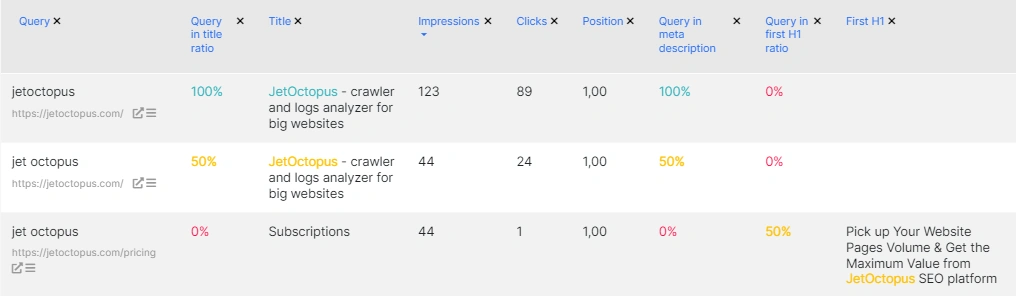
Sort those where the query does not appear in the title, meta description, or H1. Next, download the data. Filter out unique queries. Multiple pages can rank for one query, so it’s important to choose those pages to boost that are already effective in traffic. For example, you have three pages that rank in SERPs with “crawler”. One page already contains this query in the title and gets clicks, the other one does not contain the query in the title but had several impressions. Therefore, the first page can be strengthened and queries can also be added to H1 and the description to boost.
We also recommend analyzing the search volume query. If you cannot use two or three queries in H1, choose the one that will bring the most traffic.
In addition, you can use data from “Queries on Page” to create new landing pages. If there are unique queries and your website is already ranking for those queries, you can create new pages to drive traffic.
Enjoy using it!

