
JavaScript redirects: how to analyze them with JetOctopus
Most websites use server-side redirects that change the status code of the page. When a client requests a page from the web server, the server returns a permanent or temporary redirect and the new location of the requested page. However, JavaScript redirects use the window.location.replace function, which changes the URL of the requested page in the address bar of the browser, but maintains the status code of 200 OK. While Google recommends server redirects or meta refresh, it allows the use of JavaScript redirects if server redirects are not possible. With JetOctopus, you can check both server-side and JavaScript redirects that change the URL and those that do not change the status code. In this article, we will explain how to find JavaScript redirects on your website.
How to find JS redirects on your website
1. Run JavaScript crawl. Read more about settings: How to configure crawl for JavaScript websites.
2. After the crawl is finished, go to the “Technical” dashboard and select the “Statuses” data table.
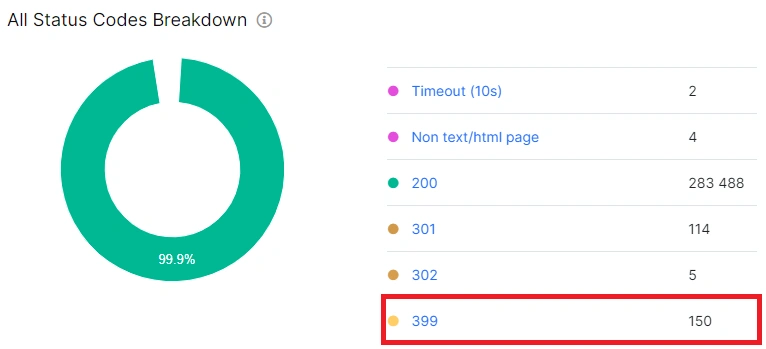
If your website has JavaScript redirects, you will see them on this chart under the number 399. Since JavaScript redirects do not have a separate status code, we have selected the rarest status code from the group of redirects so that you can see them in each technical chart.
4. Click on the segment of the chart or the number of redirects to go to the required data table. In the data table, you will see a list of pages that had redirects to other links without changing the status code.
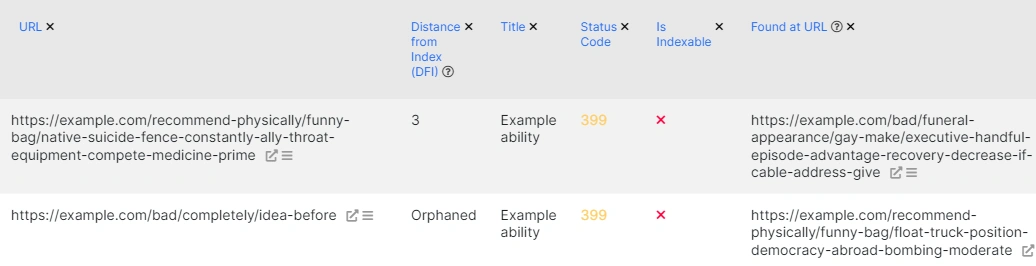
5. Click “Setup Columns” to add the redirect location URL.
Next, select “Redirect to URL” and click “Apply”.
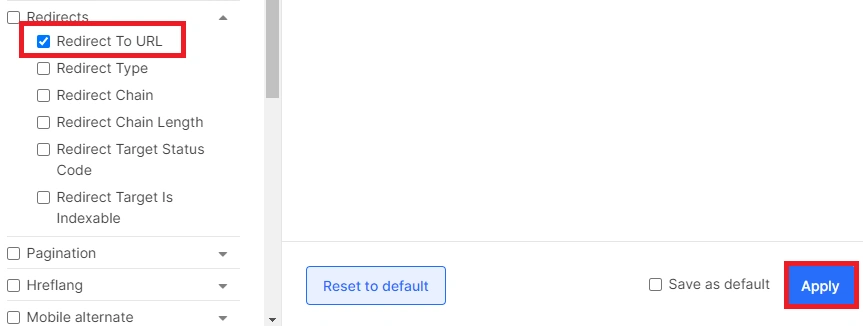
This will enable you to see not only the page with the redirect, but also the link to which the page redirects.
What to pay attention to when analyzing JS redirects
First, pay attention to whether only the pages whose content has moved to a new address are redirecting. If the page should be accessible, but the redirect is working, it should be fixed as soon as possible.
Secondly, ensure that the redirect URL is relevant and contains relevant content. Redirecting pages to irrelevant content, such as fish to meat or all pages to the home page, should be avoided.
Why is it important to detect JavaScript redirects?
Detecting JavaScript redirects is important for several reasons.
1. Google prefers server redirects with status code changes (301, 302, 307, 308, etc.). This is because Google requires more time and resources to process JavaScript redirects, which slows down website scanning. As you know, different schemes are used to scan websites with JavaScript and to scan websites with server-side rendering, and JS scanning takes much more time.
2. If the website uses JavaScript redirects, the old page will remain in the SERP longer, as Google will not replace the old URL with a new one quickly.
3. Google does not process JavaScript redirects well, and an error may occur during processing. If Google fails to execute and render the JavaScript, it may not see the redirect at all, which can negatively impact your SEO. Therefore, using server redirects is recommended, even in Google’s documentation.
By the way, JetOctopus has a lot of features for SEO of sites that use JavaScript. Here are some articles on JS SEO:
How to check JS website with JetOctopus
Why do JavaScript and HTML versions differ in crawl results?
Product Update. Compare JS vs non-JS content with JetOctopus
How to see how Googlebot renders JavaScript website

