
Understanding 429 status codes: how to handle ‘Too Many Requests’ in crawl results
In this article, we will explain what 429 response codes are, provide guidance on dealing with them in crawl results, and offer solutions to avoid this issue in the future.
What is a 429 response code?
In our comprehensive article on status codes, we extensively covered the details of each status code. However, we have noticed that many of our customers frequently encounter the 429 status code during crawls. Therefore, we would like to revisit the topic of 429 status codes and provide further insights.
The 429 Too Many Requests status code indicates a client error, specifically when the client’s web browser sends an excessive number of requests within a short timeframe, surpassing the rate limit imposed by the server. As a result, the web server, in order to prevent overloading, cannot fulfill the request and fails to deliver the page’s content to the client. Consequently, in the crawl results, you will not find titles or meta descriptions for these pages. However, it is highly probable that if you manually access the page, it will load normally, allowing you to view the content because your browser is not exceed rate limiting.
429 code status in the crawling process
Once you have configured and initiated the crawl, it is advisable to monitor its progress. Navigate to the ongoing crawl and examine the crawl progress chart, which displays the different status codes.
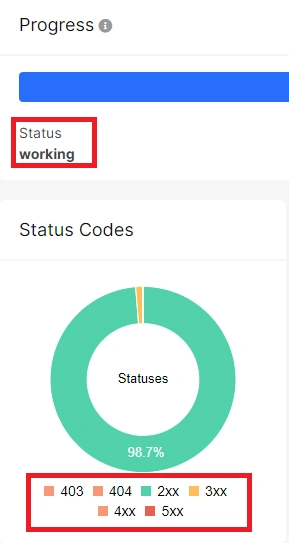
If you come across any 429 or other 4xx status codes during the crawl, we recommend pausing the crawl and reaching out to our technical support team. Consult with them to determine the prevailing status codes during the crawling process. These may include 404 (in which case the crawl should proceed as you can identify and rectify all 404 errors on your website), 403 (in which case you need to unblock the JetOctopus user agent and add our IPs to the whitelist), or 429 status codes. If the 429 status codes are predominant, consider adjusting the number of threads in the crawl. This adjustment can be made for the ongoing crawl.
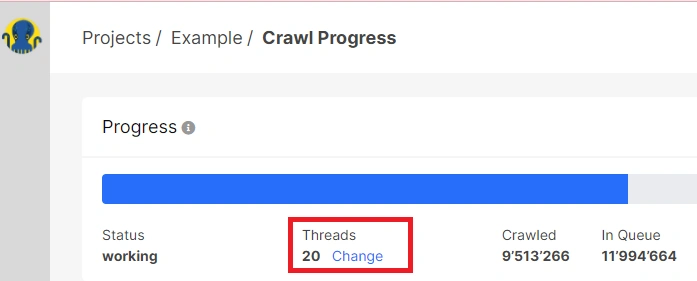
Alternatively, you can initiate a new crawl and specify the minimum number of threads during the configuration. However, keep in mind that this will impact the crawl’s speed.
What to do if the crawl contains numerous 429 status codes
If your crawl has concluded and you notice a significant number of 429 pages, there are several steps you can take to address the issue.
1. Filter all the pages with a 429 status code in the data table and initiate a re-crawl exclusively for these pages (click “Crawl the list” button), but this time with the minimum number of threads. This way, you can avoid scanning the entire website again. For more detailed instructions, refer to the article.
2. Check the presence of 429 pages in both search engine logs and user logs. When search engines encounter 429 status codes, they face two main consequences. Firstly, they are unable to access and index the page’s content. Secondly, if the number of 429 occurrences is high, search bots may reduce their crawling activity on your website. This, in turn, can impact the indexing of other crucial pages. As an example, Googlebot will attempt to revisit URLs that previously returned a 429 status code within two days. If those pages then respond with a 200 status code, Google will process them. However, if the pages consistently return a 429 status code, Google will eventually deindex them.
3. Another option is to commence a new crawl while reducing the number of threads. If you have doubts about the chosen thread count, consider conducting a small-scale test crawl consisting of 1000 to 2000 pages to ensure everything proceeds smoothly.
We insist that closely monitoring the 429 status codes in crawled pages is of utmost importance. It serves as an indicator that your web server may be overloaded and incapable of managing the load generated by both bots and users. Therefore, after a detailed analysis of 429 pages in the crawl, logs and user data, increase the bandwidth of your web server.
Where to find 429 pages in crawl results
To identify if there are any 429 pages in the crawl results, follow these steps.
1. Navigate to the “Technical” – “Statuses” dashboard.
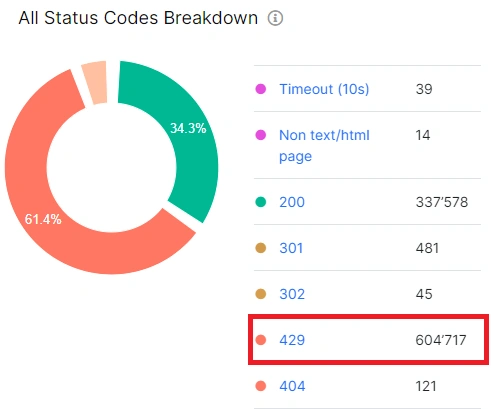
On the “All Status Codes Breakdown” chart, you will find a comprehensive list of all status codes returned by your website during the crawl, including the 429 response code. Click on the specific segment of the chart or the number associated with the status code to access the data table.
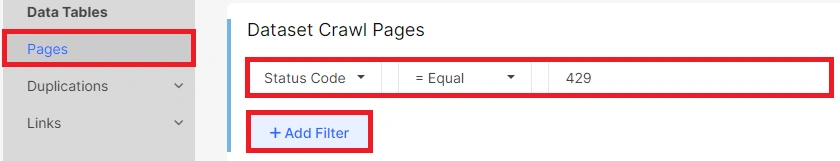
2. Additionally, you can find 429 status codes in the “Pages” datatable.
To filter the data specifically for 429 status codes, click on “+Add filter” and select “Status code” – “=Equals” – “429”. Then click “Apply” to view the filtered results.
3. If necessary, you can export all pages with a 429 status code by clicking the “Export” button and choosing your preferred file format.
By following these instructions, you can easily locate and analyze information about pages that returned a 429 status code during the crawl process.
Conclusions
It is crucial to check the 429 status code because it serves as a valuable indicator of potential issues with the web server’s capacity to handle the load from both bots and users. By closely monitoring and addressing the occurrence of 429 status codes, website owners can prevent overloading, ensure optimal performance, and maintain smooth user experiences. Neglecting to address these status codes may result in search engines being unable to index pages properly and could have a negative impact on the indexing of other important pages. Therefore, regular checks and appropriate actions are essential to maintain a healthy website infrastructure.

