
How to check canonicals with JetOctopus
Rel=”canonical” is a powerful method that allows you to manage duplicate content. When you use the canonical, you tell search engines which page to show in search results.
However, there are situations when due to the incorrect use of the canonicals, unwanted pages are displayed in the search results or, conversely, the most important ones drop out from SERP. For example, instead of a category main page, a pagination URL is in the SERP. This situation can increase the bounce rate, because the first page contains the latest content that brings the most benefits to visitors. And on the pages of pagination may be outdated data, in particular, the goods which are not available.
Using JetOctopus, you can audit canonicals quickly and easily. We have created several reports with the most common problems.
Step 1. Start a new crawl or select from the list the crawl you want to analyze.
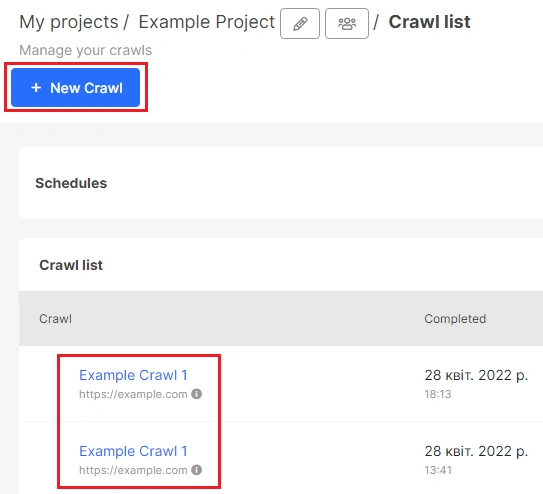
Note that canonicals are also used if you have a separate mobile subdomain. You can enable a special scan mode for such websites while crawling. Using this scan mode, JetOctopus will process canonicals in a special way.
Step 2. Wait for the crawl to finish.
Step 3. Analyze the canonicals in the following reports:
- Indexation;
- Rel tags.
Indexation
In the “Indexation” report, you can see the number of canonized, or non-canonical, urls. Non-canonical pages contain a link to a different url (canonical url) inside the rel canonical tag. Canonized urls contain similar content to canonical urls, so they should not be shown in the search results.
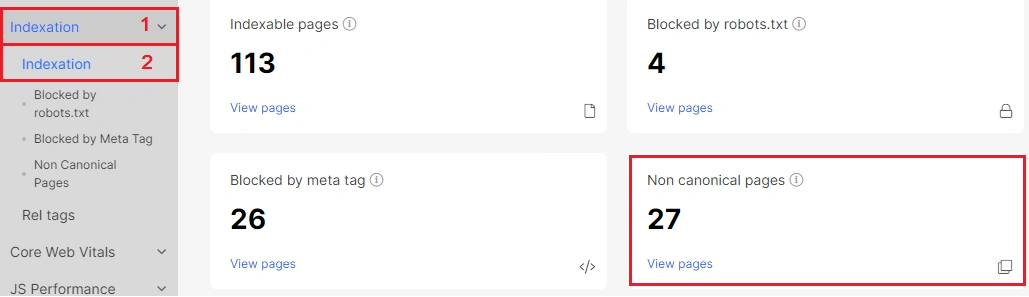
If you click on “View pages”, you will go to the data table.
We have created the “Non Canonical Pages” report separately for your convenience. This data table contains a complete list of canonized urls with 200 response codes.
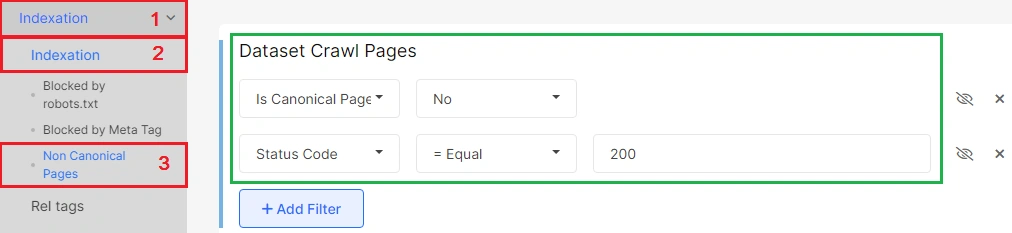
Check it out whether this list contains only those urls that should not be in the search results.
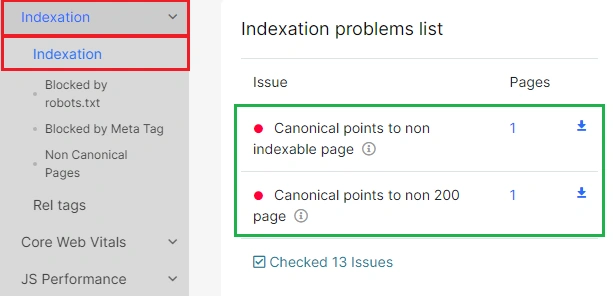
Also, in the “Indexation” report you can find the list with the most common problems with canonical.
- Non indexable self canonical page – self canonical is used to confirm that the current page is unique and that it should be shown in search results (the link in the rel canonical tag should be the same as the url of the scanned page). The page with non-indexable self canonical has meta robots or X-Robots-Tags that prohibit page indexing. This is a controversial rule for search engines. Therefore, they will automatically select a more restrictive rule and drop out the page from the SERP. If you want to see this page in search results, change indexing rules.
- Multiple canonical tags – you will see this problem in the list if there is more than one canonical tag in the page code. This can be a problem during indexing, as search engines will not be able to select the correct canonical url.
- Canonical points to non indexable page – as in the situation with “Non indexable self canonical page”, this one can create problems with search results. By using a canonical with a non-indexable URL inside, you are giving a conflicting signal to the search robot. On the one hand, you indicate that the current url contains similar content as the canonical url. Therefore, the canonical URL should be shown in the search results. On the other hand, you signal that the canonical URL does not need to be shown in search results. As a result of this error, both urls will be dropped out of the search results with high probability.
- Canonical points to non 200 page – another controversial signal for search engines. This combination shows that the broken url must be in the results.
Rel tags
In the “Rel tags” report you will find general information about canonicals. In particular, the number of pages in the code with rel = canonical.
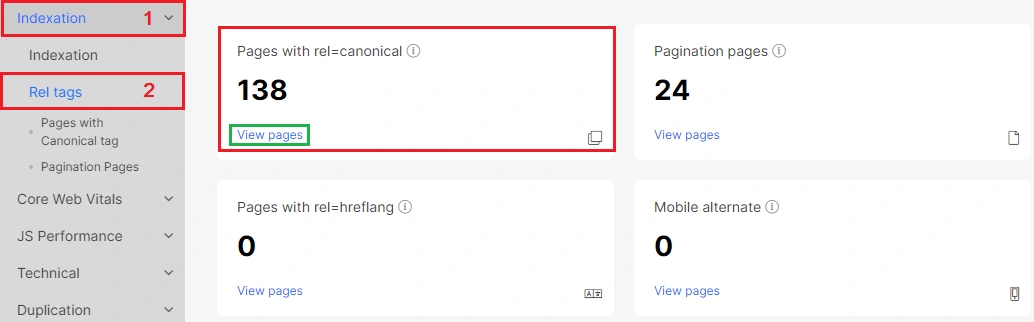
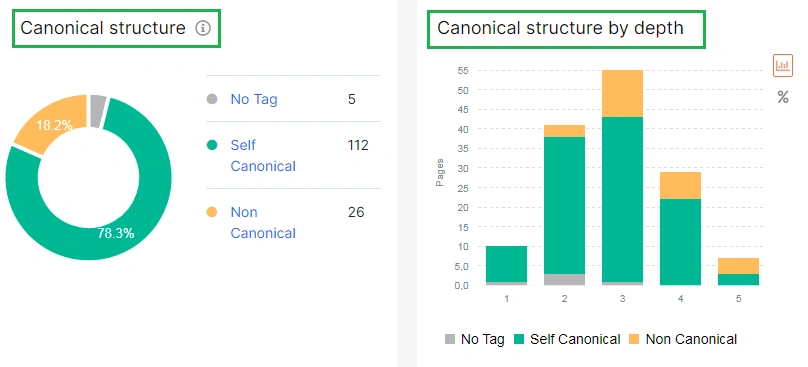
In the report “Rel tags, you can explore the structure of canonicals on your website and compare the number of canonicalized and self-canonical pages.
Separately, we created a data table with all the pages that contain rel=canonical in the code.
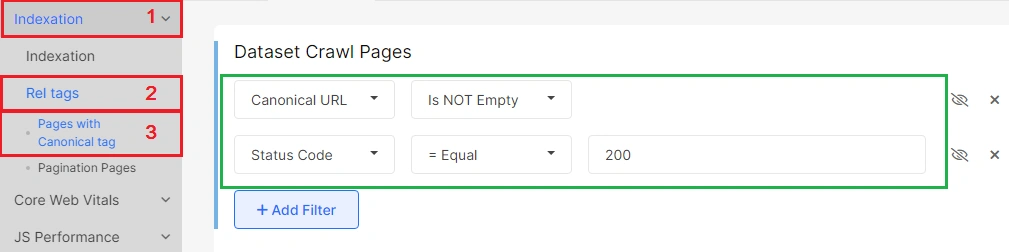
Step 4. Analyze the canonicals in the data tables.
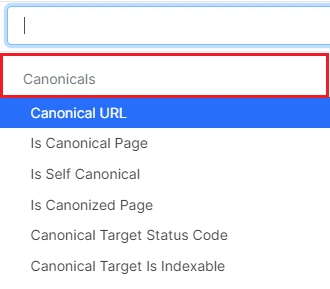
Go on to the “Data tables” – “Pages” report. Click the “+ Add Filter” button to select the desired urls for analysis:
- Canonical URL – select which URL should be inside rel-canonical, for example, with subdomain;
- Is canonical page – whether the page is a main version and whether you want to see it in search results;
- Is self canonical – the canonical tag contain a link to itself;
- Is canonized page – select “Yes” to see pages that contain canonical with other urls inside the tag;
- Canonical Target Status Code – select the response code which the url inside rel canonical tag returns;
- Canonical Target Is Indexable – does the url inside a canonical tag open for indexing.
The ability to compare canonicals in the regular HTML and the JavaScript versions is very useful.
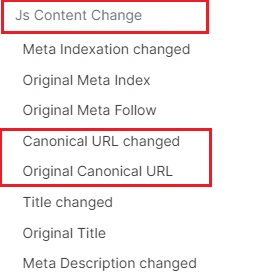
To do this, go to the filtering block “JS content change” in the “Data tables” – “Pages” report and select:
“Canonical URL changed” – if you want to see which canonicals differ in the regular HTML code and rendered JavaScript;
“Original Canonical URL” – select this option to filter canonicals (which was found in the original source code): you can find empty or relative canonicals, and so on.
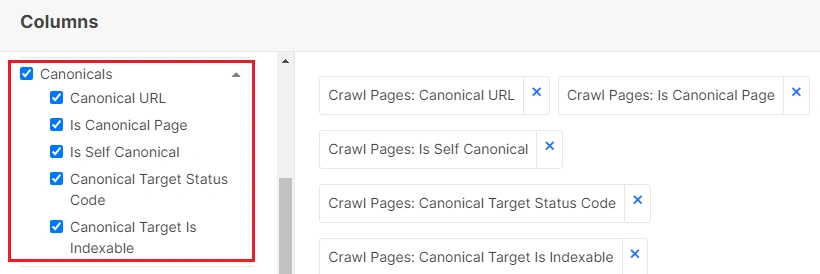
Step 5. Adjust the columns.
Click “Setup columns” to add the required data to the table.
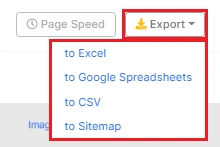
Step 6. Bulk export the data.
Click the “Export” button to download CSV, Excel, or Google Sheet.
Step 7. Save the selected data table as a problem, create a KPI, or save the list for re-crawling.
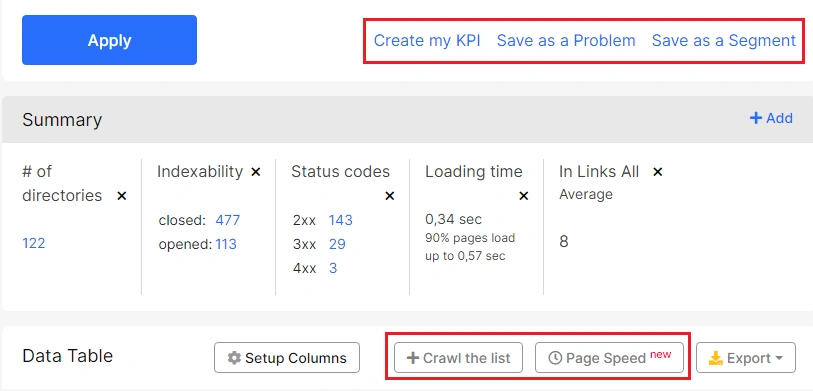
“Crawl the List” – you will go to the crawl configuration page, where all the urls from your filtered data table will be saved. You can run a recrawl to see if the problem is resolved.
Click “Page Speed” to start analysis of the Core Web Vitals metrics for this url list.
“Create my KPI” – create a goal to work with selected pages.
“Save as a Problem” – save the selected urls as a problem. It is very convenient to create a list of problems based on the results of the crawl and prioritize them.
“Save as a Segment” – save the url list as a separate segment, which you can use in all reports, charts and visualizations without additional settings.
Step 9. Conduct additional canonical checks
With JetOctopus, you can perform additional checks:
- check if you are using full (absolute) url in rel = “canonical”;
- whether you use the correct HTTPS protocol in the canonical tag;
- whether you have no canonicals to external sites and many others.
Canonical is a powerful tool that you can customize for each site. So try, in addition to common problems, to find non-typical canonicals in the results of the crawl purely for your website.
More information: How to canonize URLs. Dos and don’ts

