
Segmentation SEO For eCommerce Website: How to Skyrocket Your Rankings
Data analytics plays a crucial role in SEO, especially for eCommerce businesses with a vast number of site pages. For eCommerce, a generic SEO strategy may work but will not be as impactful and profitable as a well-thought-out “divide and conquer” SEO strategy. In other words, we’re talking about a segmentation SEO strategy.
With segmentation, you can divide your eCommerce site into smaller, more logical parts using different datasets. You can then analyze these segments with their individual report and implement various changes as well as monitor the dynamics of improvements needed to have a much better impact on organic search rankings and conversions.
In this comprehensive guide, let’s look at how segmentation can help you improve your eCommerce websites. You’ll also learn how to use JetOctopus to build segments using different datasets and filters.
What is Segmentation, and how to use it for SEO?
Segmentation refers to the process of dividing and grouping your site’s data into smaller, meaningful segments and analyzing these segments’ individual reports to find the most as well as the least effective part of the website that needs work.
Using JetOctopus’ segmentation tool, you can crawl and segment your website with the help of different datasets and its easy-to-use filters.
The best part is that you do not have to crawl your entire website again for every segmentation. You only need to crawl once, and you can then divide your site’s data into as many segments as you’d want to.
This is especially useful for large eCommerce sites with multi-section domains and hundreds of product pages. SEO techniques can then be much easier to implement. Moreover, when you’ve built different segments you can analyze and view all the reports of a particular segment, not the general picture of the whole site within JetOctopus.
Here is an example to explain this better:
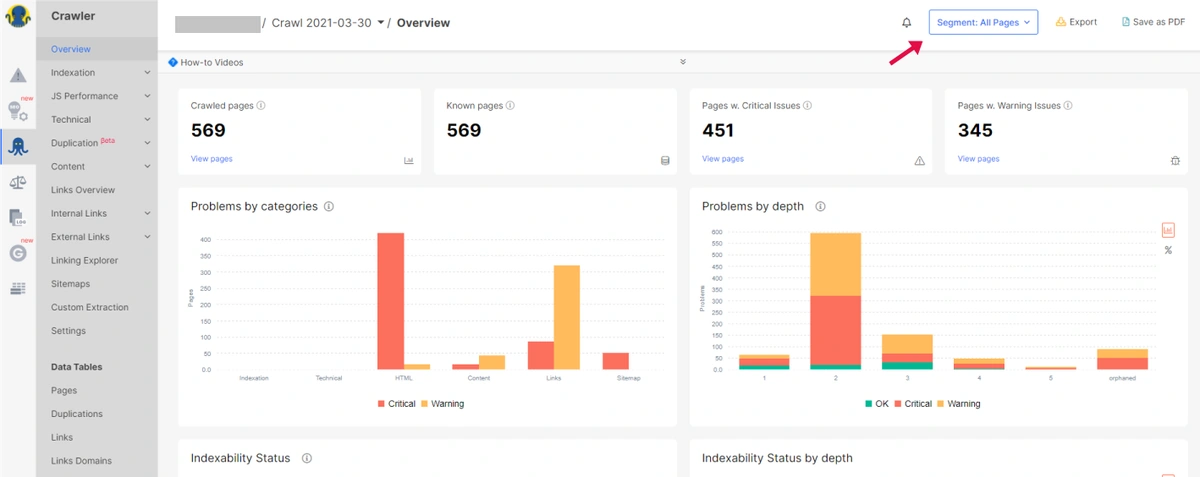
When you crawl the whole website you can view the All Pages Crawl report, here in the above example you can see there are about 569 crawled pages in total with 451 having critical issues and 345 having warning issues.
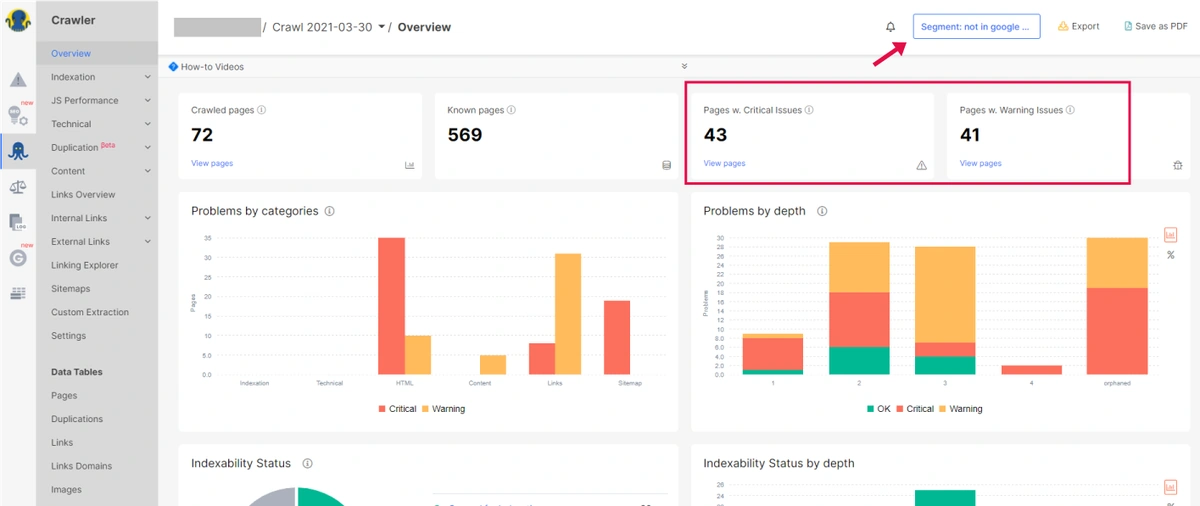
But when you segment it with Pages that are not in Google Search Console (not getting impressions), you can see there are only 72 pages that are not in GSC in which 43 pages have critical issues and 41 pages have warning issues.
This way you can slice apart your whole website to look deeper into a particular segment and easily analyze it through reports.
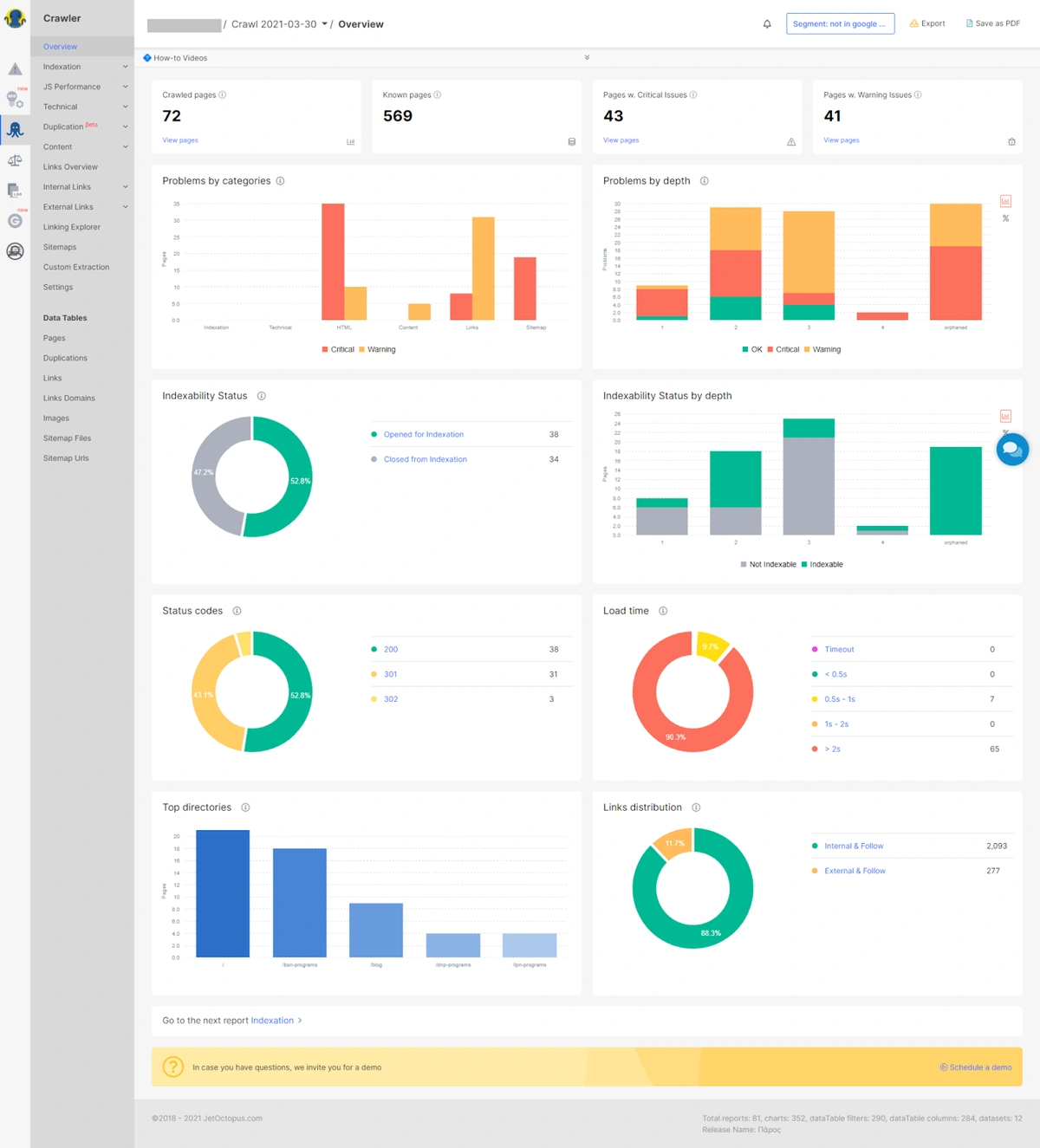
Every single segment will have its own individual report as shown above, which will help you analyze all the issues in detail such as indexation issues, crawl issues, bot behavior, etc, and monitor the dynamics of improvements in each particular segment.
The tool has many datasets like the log data, crawl data, Google Search Console data, Google Analytics data, and more to compare and select pages with over 120 different filters of URL, canonical, redirects, pagination, lang, mobile, technical, JS performance, indexation, content, duplications, system hashes, links, meta, etc. to work with.
Segmentation SEO can also help you:
- Analyze complex data joins between different data sets, which otherwise would not be possible with Excel sheets.
- Do a much quicker and easier analysis of SEO issues and identification of next action steps to tackle these issues.
- Experiment with different segments to find new ways to improve organic search engine performance and website conversions.
What are Datasets?
Datasets play a vital role in segmentation, and it is crucial to understand their importance. The filters, as discussed in the previous section, are taken from different datasets. The more datasets are integrated into JetOctopus, the more diverse segments you can build.
These datasets are different groups of organic search engine performance data from where you can use different filters to build segments.
Here are few datasets, you can add:
- Crawled pages – Pages found in your site structure.
- Logs pages – Pages found in logs, which means these pages are getting visits from search bots.
- Google Search Console pages – These pages are found from data in GSC, meaning that these pages are getting impressions and/or clicks on Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs.)
- Google Analytics SEO Visits – Pages from Google Analytics with SEO visits.
- Google Analytics PPC Visits – Pages from Google Analytics with PPC visits.
- Ahrefs backlinks – Backlinks data from Ahrefs tool.
- Google Search Console queries – Queries data found in Google Search Console.
How to use Segmentation for eCommerce websites?
Approaching SEO for large eCommerce sites can be overwhelming with more pages than you can even get your head around and issues like product variants, complex filtering systems, and out-of-stock products.
SEO for eCommerce sites requires a different kind of SEO strategy. Through segmentation, the sites can be broken down into smaller parts to analyze particular issues.
Here are some examples to explain how segmentation can be highly effective and beneficial for eCommerce websites:
Simple segmentation use-cases for eCommerce websites:
- Product pages – You can segment product pages by finding URLs that contain “products” or keywords of a particular product in them.
- Pagination pages – The website can have multiple pages containing multiple products, so one can check pagination pages.
- Blog pages – These can be pages that contain “blog” or subdomain of “blog.”
More complex examples of segmentation use-cases for eCommerce websites:
- Product pages with duplicate titles – URLs that contain “products” and have title duplication.
- Thin pages – Pages with the number of words < 100.
- Poorly linked pages – Pages with internal links All < 10.
- Trash auto-generated shopping cart pages – Pages with titles that contain “shopping cart.”
- Out of stock products – Pages with titles that contain “out of stock.”
How to Build Segments in JetOctopus
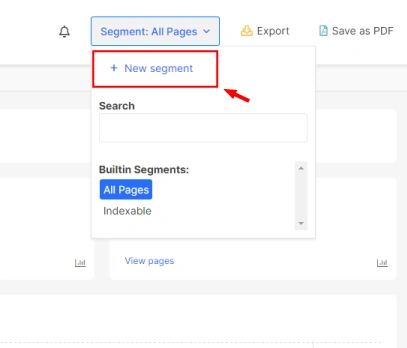
For using the segmentation tool, you can head over to the + New Segments in Segment: All Pages in the upper right side of the header.
Here you can start using the filters to create new segments.
Use cases of complex segments that you can use for your own eCommerce website
By creating segments based on the filters shown, you’ll be able to separate site pages and analyze them easily. Below are a few use-cases of segments you can use to analyze different issues.
Pages that are in site structure, receiving search bots’ visits but don’t get impressions in SERPs.
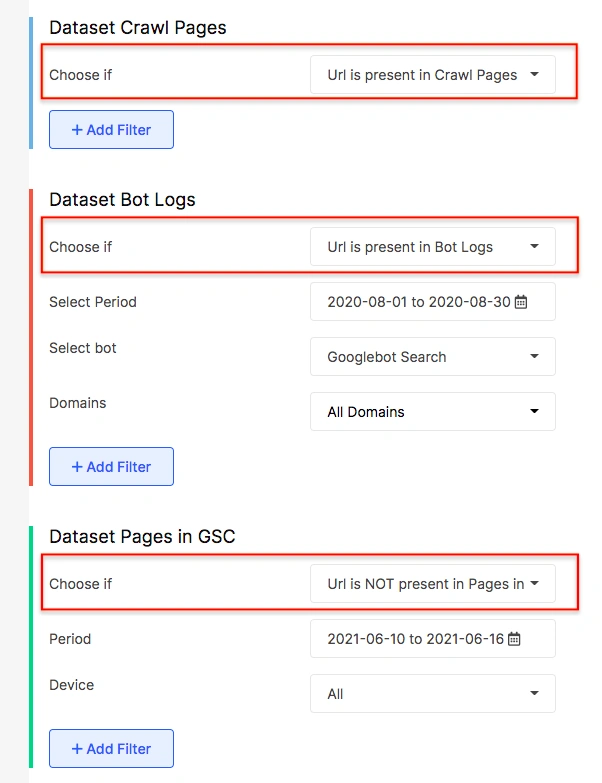
By selecting the options as depicted in the screenshot above, you will find the pages that are visited by bots and are in site structure but are not in Google Search Console.
Such pages will be in your website structure and will be getting crawled. But, these pages will not be getting impressions and clicks on the Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs.) These pages will not be effective in terms of SEO as they have no impressions from search engine users.
You can analyze these pages and understand the underlying cause. You can improve these pages by optimizing them for the right, intended keywords. In the case of legacy pages that are of no use, you can entirely get rid of them.
The orphan logs
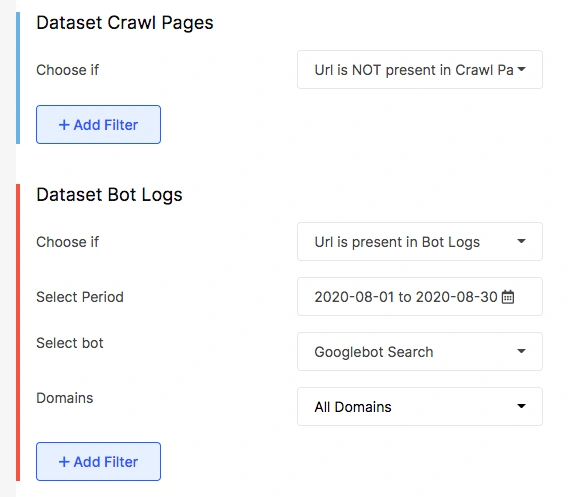
When you will apply this use case you will find pages that are visited by bots but will not be in your site structure.
Such orphan log pages are found on sitemaps but not found by the crawler as these are not a part of your site structure. The Crawl budget is spent on these pages and it is important to get the issues fixed as soon as possible.
Such pages are not present in the site structure, meaning there are no links pointing to these sets of pages. You can strategically place internal links to these pages from your site structure.
The orphan max
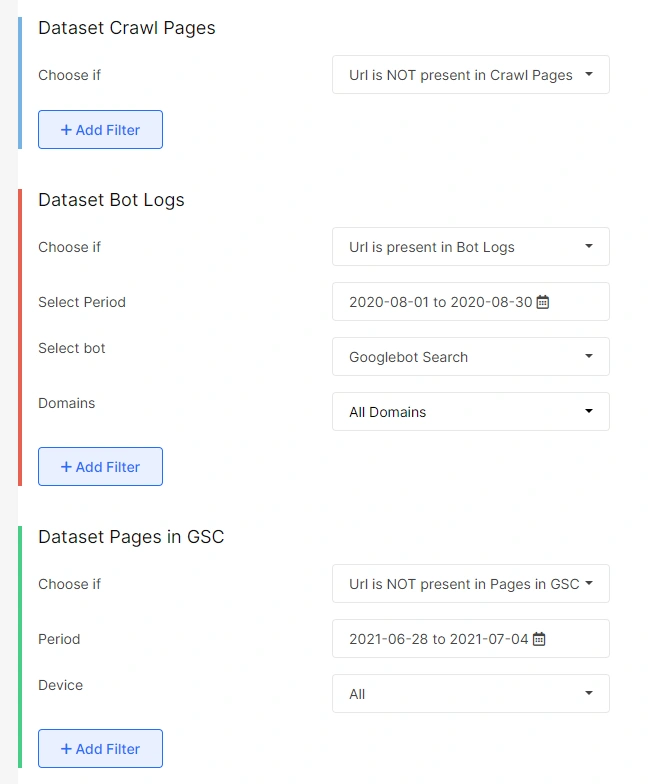
Orphan max pages are those that are getting bot visits but are not present in the site structure. These pages will also not be getting any impressions or clicks on SERPs as per the data from Google Search Console.
It is important to find such pages which are visited by bots but are not in any other datasets. You can remove these pages from indexing if they are not important as the crawl budget is wasted here, and they are not effective in terms of SEO.
The orphan pages which are getting organic traffic
Orphan pages are pages that aren’t linked anywhere on your site. Because there are no links to them, website visitors and site crawlers won’t be able to find them either.
So, how do you find orphan pages?
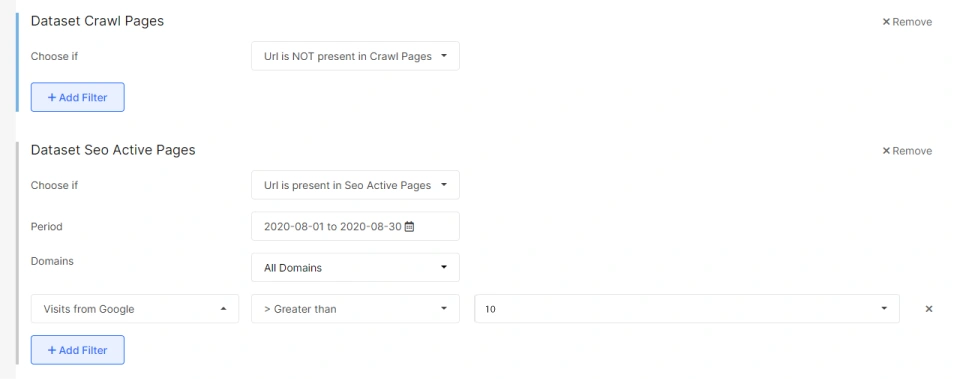
When you look closer, you’ll find that the crawl budget is being spent, and these pages will be getting traffic, but they will not be in the site structure. So, you shouldn’t ignore these pages as these can be highly valuable.
You can start by analyzing these pages deeply and deciding whether they are of any value. If yes, you should take them into the site structure. In case these are legacy pages or trash pages, you should consider closing them as they do not add any value.
The “not working sitemap” pages
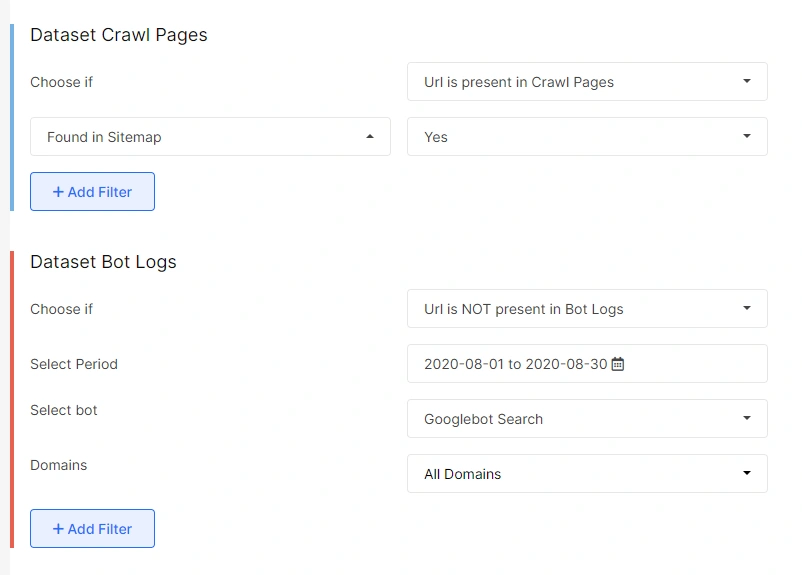
The “not working sitemap” pages are those that will be a part of your sitemap. However, these pages are not getting crawled by any search bots. This can be a serious SEO issue, and you should redirect this to your developers to get these issues fixed immediately.
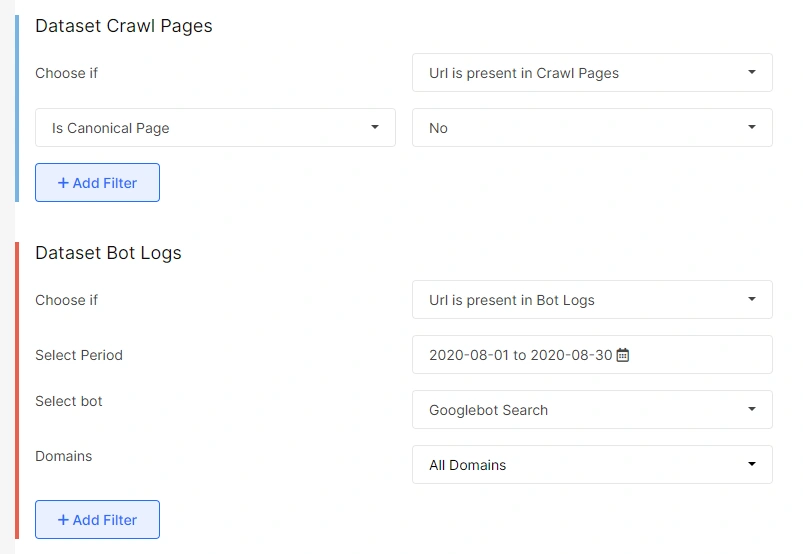
Pages that are wasting your crawl budget
Non-canonical URLs are pages that are a canonical duplicate of another URL. Or these can also be duplicate pieces of content. Since these are just duplicate pages, ideally, search bots should not be visiting these pages.
If the URL of the crawl page doesn’t match the canonical URL, then these are non-canonical pages where your crawl budget is being wasted.
If search bots are visiting the non-canonical pages on your site, then your crawl budget is being wasted on these. In the case of large websites with thousands of such non-canonical pages with bot visits, a massive amount of crawl budget may get wasted, which is not good.
You can save your crawl budget by adding a canonical tag to these pages. This way, only the main pages will get search bot visits, and your crawl budget can be saved.
The pagination issues
Another type of SEO issue can be caused by pagination pages further than 20, which are being visited by search bots and are present in your site structure. By using the GSC filter, you can find that these pages may also get impressions and clicks on SERPs, which is not ideal.
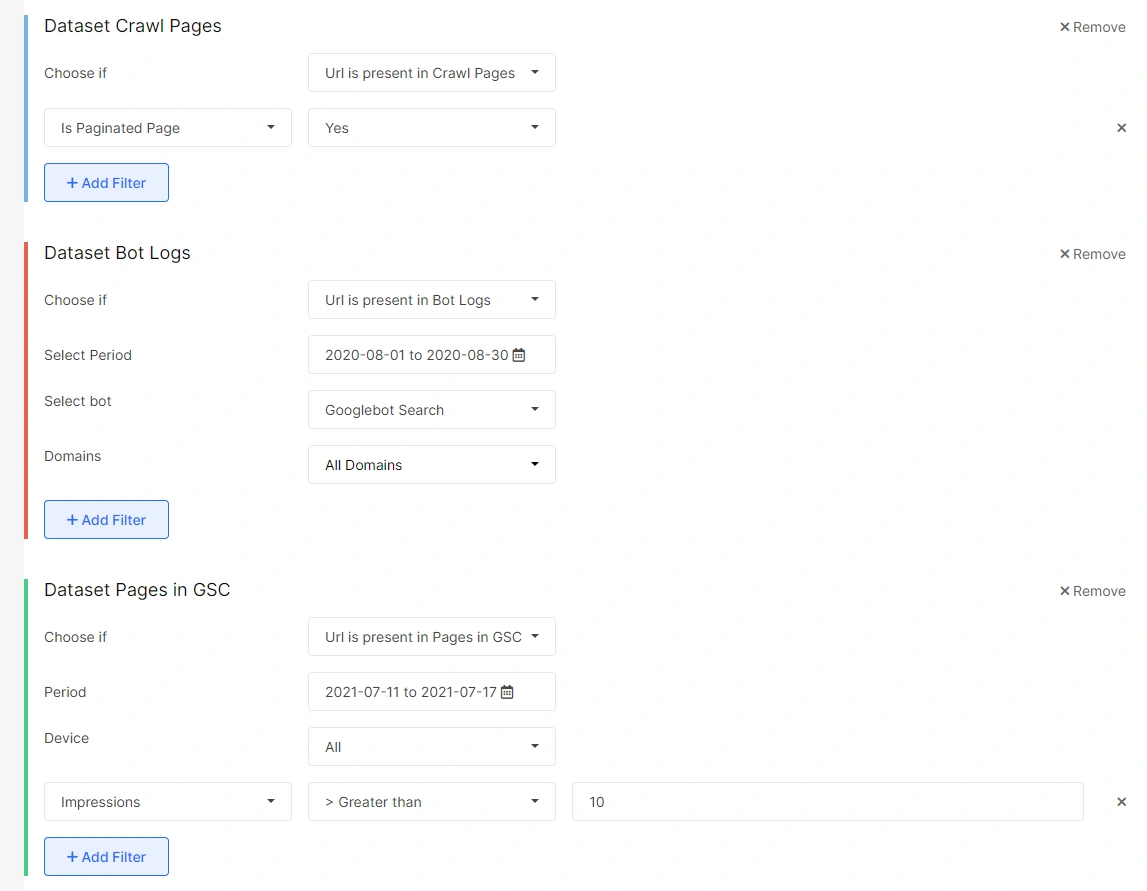
You can segment such pages using the filters as depicted in the screenshot above and fix such pagination issues by restricting their access from search bots and removing them from your site structure.
The non-crawled pagination issue
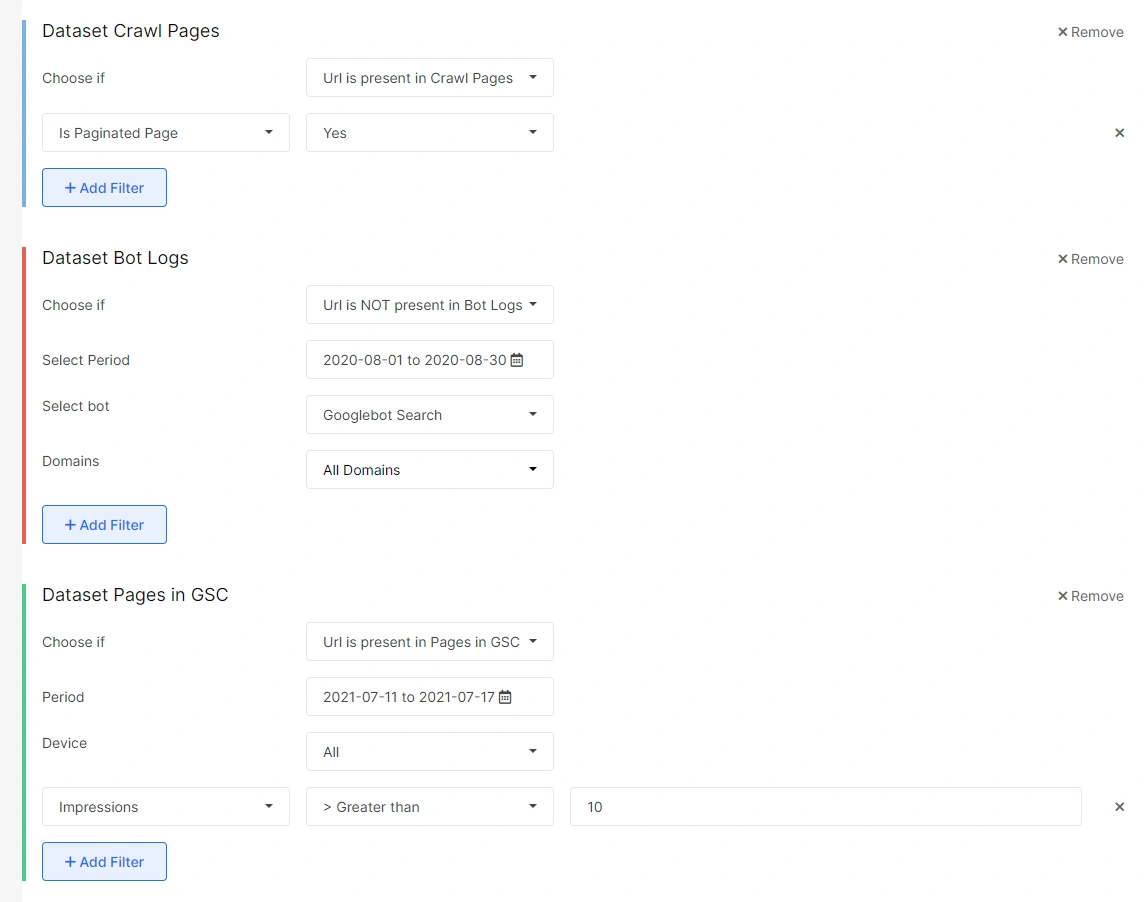
Another type of pagination issue may be encountered when pagination pages further than 20 have impressions but are not visited by search bots. It is important to handle these pages the same way as in the previous section. You can do this by removing such pages from your site structure.
Final thoughts
SEO implementation, especially technical SEO, for large eCommerce sites can be overwhelming without any fruitful results. Segmentation using the JetOctopus tool can be a great way to tackle this problem. Also, in large companies, there are often many teams testing and experimenting with new parts of the website. They can use JetOctopus to segment parts of the website and see if the changes are impacting the rankings or not.
Using segmentation, you can divide your site’s data into meaningful segments and use a “divide and conquer” SEO strategy to get much better organic search engine performance. You can also monitor the improvement dynamics after implementing needed changes by segments, not the general numbers on your entire eCommerce website.


