
What is DFI (distance from index) and how to analyze it
As you know, internal linking is extremely important for users of your website and of course for search engines. All visitors, even artificial intelligence, want to access any page of your site in just a few clicks. And the simpler and clearer the path from the home page to the desired one, the better the user behavior metrics will be. And the better search engines will index your website. One of the indicators of clear navigation and internal linking is the distance from the index.
What is distance from index
The distance from index is the number of clicks that must be made from the home page to the desired one. For example, the domain is the home page with DFI 1. From the home page, the user goes to the category page, the DFI is 2, and from the category page to the product page with DFI 3. And on the product page, the user can click on the product reviews page. Its DFI is 4. If the user switches to a separate review, then its DFI is 5.
https://example.com – home page, DFI 1
https://example.com/category/teapots – category, DFI 2
https://example.com/teapot-bestbrand-1l – product page, DFI 3
https://example.com/teapot-bestbrand-1l/reviews – reviews, DFI 4
https://example.com/teapot-bestbrand-1l/tommy-review – separate review, DFI 5
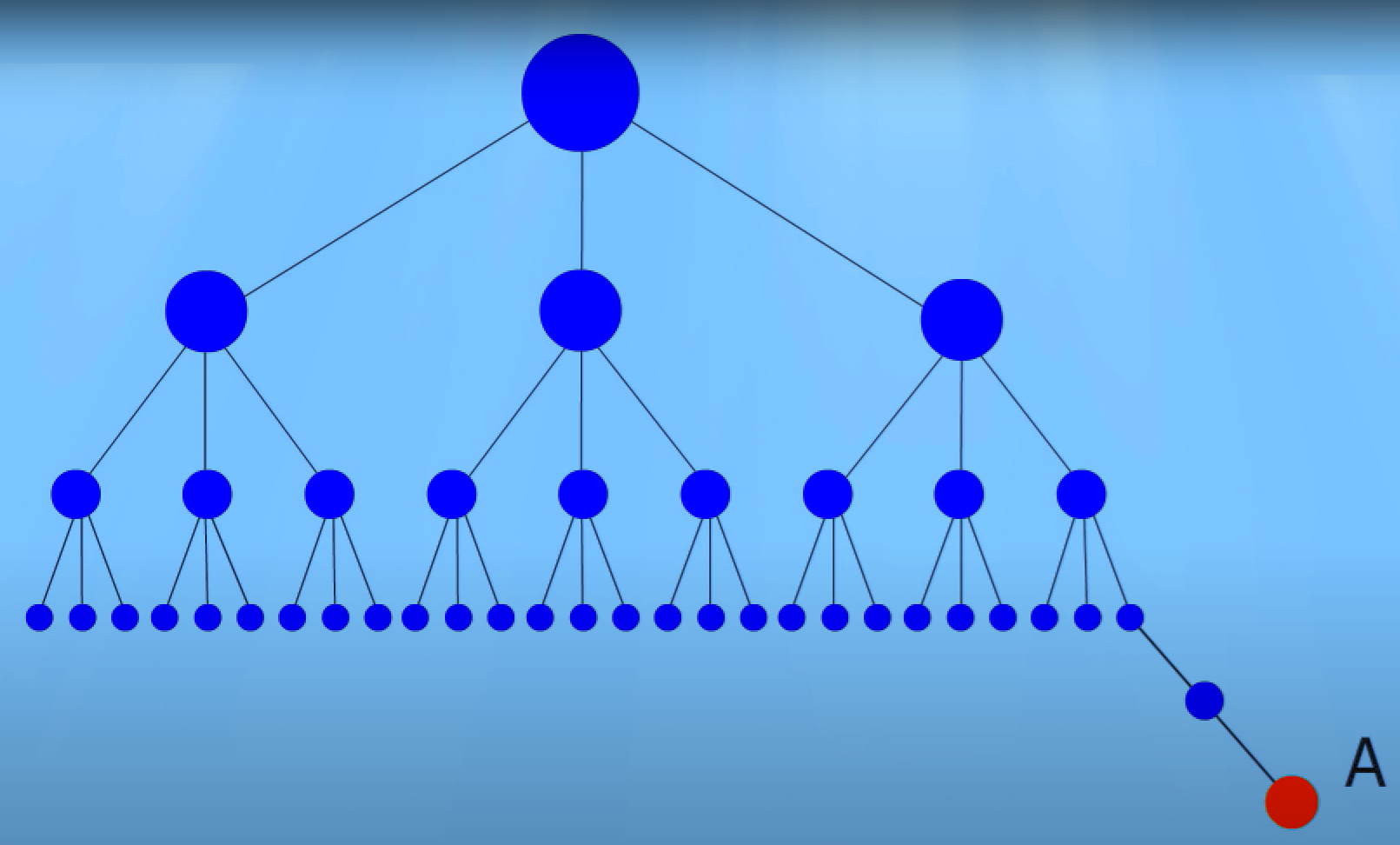
The distance from index is not the same as the number of slashes or subfolders in a page’s URL. After all, your category page can have three subfolders in the URL, and the DFI will be 2.
https://example.com/en/category/teapots – three slashes, DFI 2.
Why do you need to monitor DFI? Clear and understandable navigation is essential for scanning and indexing your website. And the deeper this structure is, the more difficult it is for search engines to find and crawl pages with the lowest DFI.
This issue is especially relevant for websites with millions of pages. After all, each website has its own crawling budget. So, search engines scan a certain number of pages regularly, according to search demand and trends. And if the number of pages is large at the first levels, then the search robot is less likely to scan pages with DFI 6, 7 and more, because there is not enough crawling budget for deeper scanning. As a result, only part of the pages of your website will be shown in the SERP.
How does it work with branded traffic? For example, you have a large e-commerce project. Users know your website well and often search for something like “your website + buy something”. In this way, users tell search engines that they want to go to a page on a particular website that sells something. But if the required page had DFI 8, for example, then most likely the search robot did not scan it and showed in the SERP the most similar page of all those it scanned. In some cases, a user will click on your website and find what they need using internal search. And in some cases the visitor will go away. You will lose money because the user will not make a purchase.
Another example. You have a page where all questions about delivery and payment are collected. The DFI is like this: “Home page” – “FAQ” – “Delivery” – “Information about international delivery”. Then the user must click on a certain question with a separate URL – DFI is 5. With this structure of URLs, there is a possibility that not all pages with certain questions will be scanned. And if a user searches in Google for an answer about whether you deliver on the next day to Canada, SERP will have a general page with all the answers. The user will have to visit the page with general information, find the right question and make a few more clicks to get an answer. But as research shows, each additional click makes the transaction less likely.
As we can see, DFI is related not only to scanning by search engines, but also to the behavior of users on the website. Pay attention to how visitors click through the pages of your website. This data is available in Google Analytics. What pages does the user visit? Do visitors often make conversions on pages with more than 5 clicks from the main page? And more than 10 clicks? This is very interesting to explore.
How to analyze DFI on your website
During crawling, JetOctopus collects information about the distance from the index. So, you can get information about the structure of your website and how crawlers scan your website depending on the DFI in a simple way.
You can find information about DFI in the “Logs” and “Crawl” sections.
For analysis, go to the desired crawl. Let’s start with the indexation analysis. What do we see in the diagram? That even on the 6th and 7th levels of the DFI, there are many indexable pages.
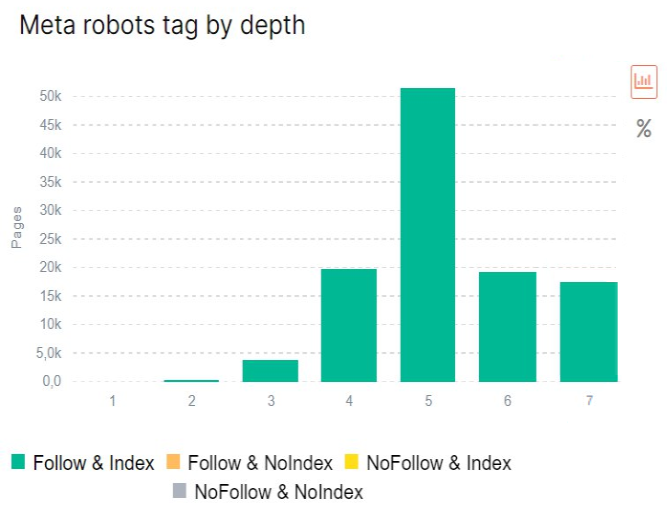
Please note that all charts labeled “by depth” show the distribution of problems by DFI. That is, you see the distribution of data depending on the number of clicks from the homepage of your website. If you used a start URL other than the home page when configuring the crawl, the DFI will be calculated from the URL you entered during the settings.
Now let’s go to the logs and find out how search engines crawl the pages of your website depending on the DFI.
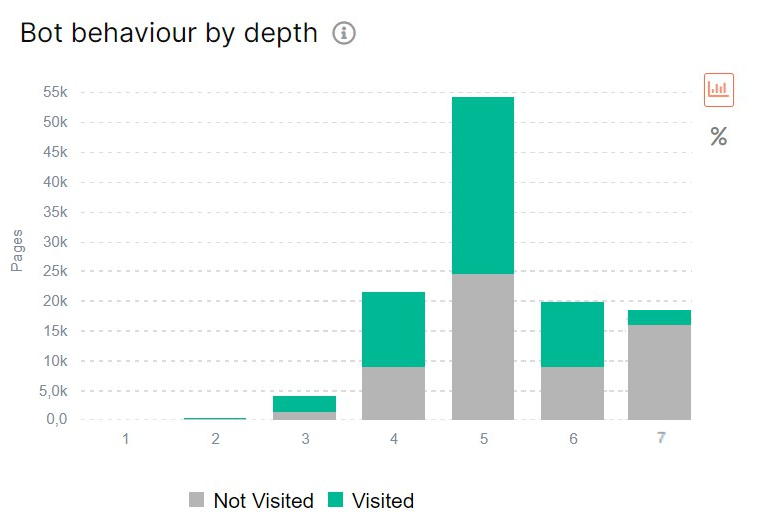
There were about 20000 indexable pages with DFI 6. But only 10 thousand of them were visited by search bots. And for DFI 7, the number of visits by search robots is even less.
If crawlers don’t visit the page, the page won’t appear in search results.
The next step is to analyze pages that have a DFI 6 or more. Of course, the critical DFI may be different for each website. Critical for you will be if the number of indexable and scanned pages differs by a factor of two.
Go to crawl results – “Data tables” – “Pages” dataset.
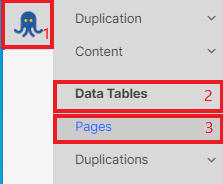
Click the “+Add filter” button and select “Distance from Index (DFI)” – “> Greater than” – “5” and “Apply”.
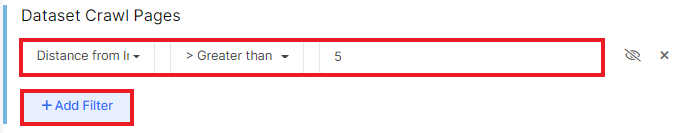
In the results, you will see a list of pages with a DFI greater than 5. You can also combine segments and select pages that were in logs (“Bot Logs”) or that had impressions in Google (“Pages in GSC”).
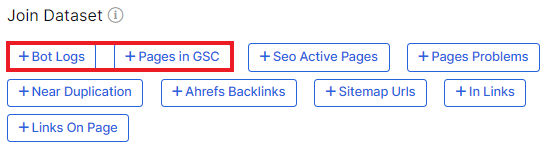
Or use a segment of indexable pages.

What to pay attention to when analyzing pages with critical DFI?
1. How search robots visit pages, depending on DFI, and how many clicks and impressions these pages have as a result.
2. Analyze the internal linking of these pages. Use “Linking Explorer” tool.
More information: How to use the Linking Explorer tool.
Maybe you need to improve the internal linking.
3. Select several pages with the critical DFI and analyze them using Google Analytics. Which traffic channels are most effective, how users find these pages, the way and clicks, etc.
4. Content of the pages – what information is there, whether it is important, whether these pages are needed in SERP.
Depending on the results of the analysis, create a strategy that will help search engines and visitors to find faster and better interact with all pages of your website.

