
Importance of Ranking Signal Consolidation, Web Entity Hierarchy and Clean URL Structure for Better Communication with Search Engines
In this SEO Case Study, with the help of SEO Theories, Practices, and Concepts, we will explain how a simple URL structure, a clear and logical Site Hierarchy including Faceted Navigations and Filter Structure, and Technical SEO can create 296% Organic Traffic Growth concretely with an example of Health Products Brand’s SEO Project.
This SEO Case Study belongs to Turkey’s largest sexual health products manufacturer. Censorship has been used to conceal the identity of the firm and secure its internal data. We will mostly refer to the relevant company with the term “brand”.
Ranking Signal Dilution (or Consolidation) is an important SEO Term that is related to the outcomes below:
- You will see how SEO Theories and Theoretical Information and Technical SEO can create 296% Organic Traffic Growth in YoY Comparison. (Between 1 Jun – 1 September 2019 and 1 Jun and 1 September 2020.)
- It can increase your organic traffic by 35,51% in one month.
- It can create 33,33% Organic Traffic Growth in one month and 66,24% in four-month.
- Also, we will see an organic based Direct Traffic increase of 40% annually.
Also, during the SEO Case Study, you will see how I use JetOctopus for a better SEO Analysis for a deeper and more critical analysis.
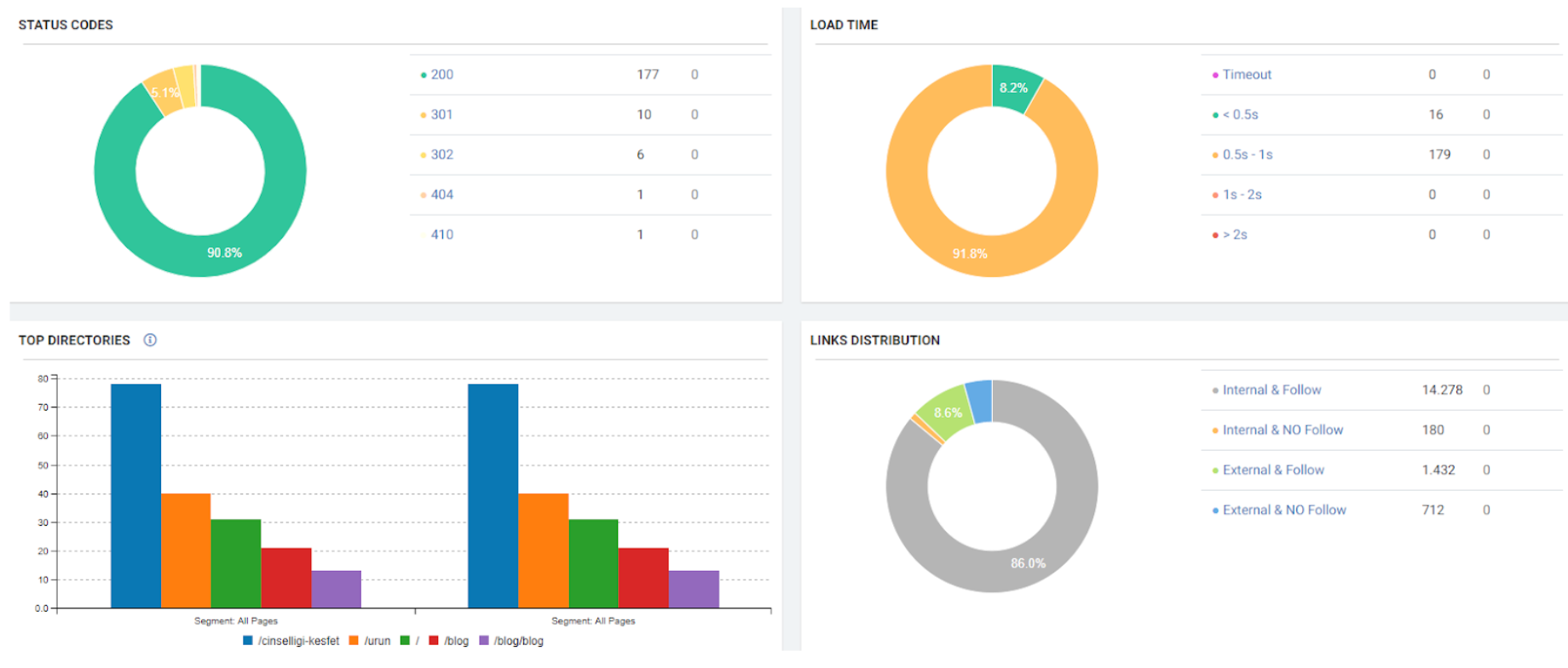
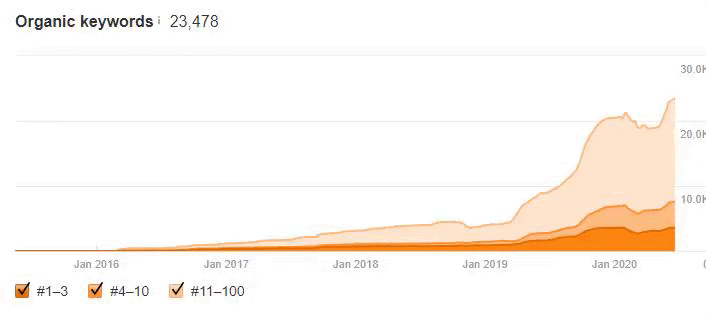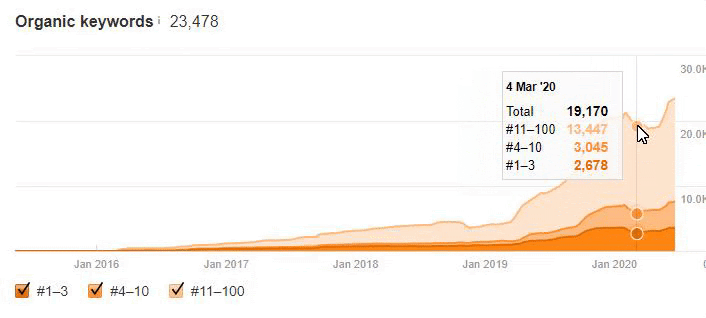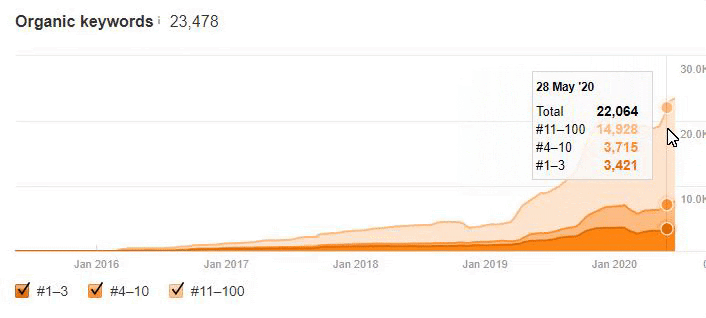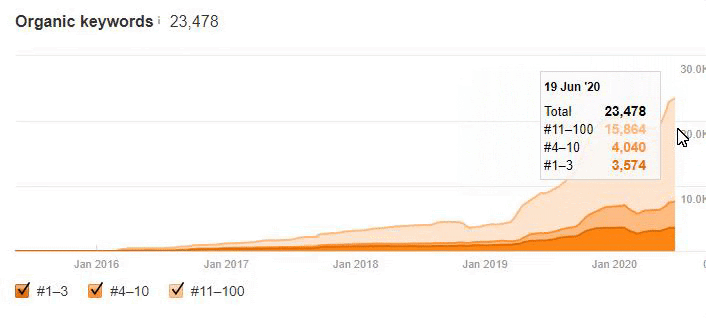
Below you will see the organic traffic increase coming to 300% on an annual basis and how the Ranking Signal Dilution temporarily reduced Organic Traffic in 2020 in a concave form.
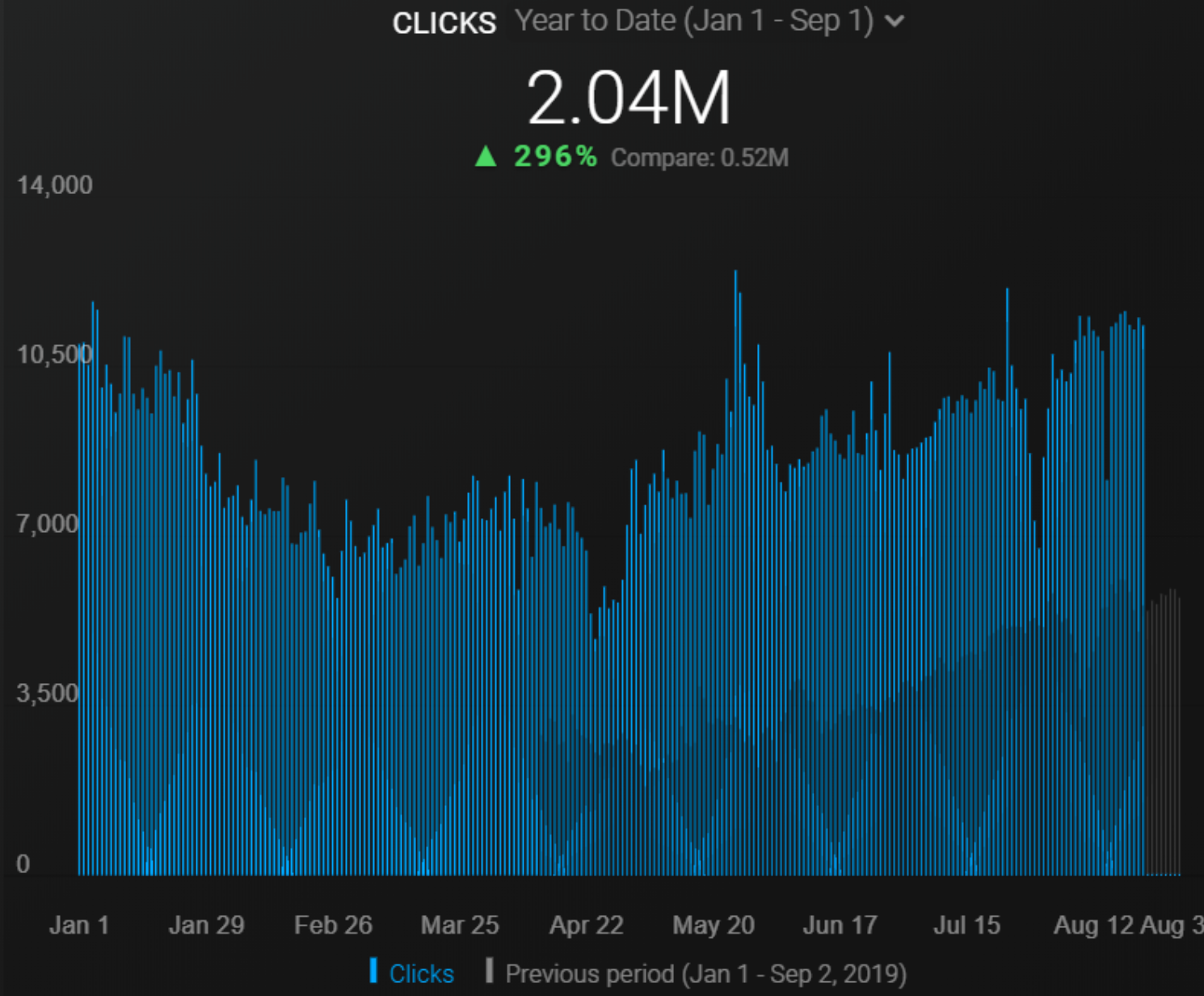
The Chart above shows the “Year-to Date” comparison on an annual basis. In addition to an organic traffic increase of 296%, organic traffic appears to have declined significantly in February, March and April this year.
The main reason for this decrease is a design and site-structure change that does not take into account the concept of Ranking Signal Dilution. After solving the problem, Organic Traffic increased by 33.33% in the first month (in May compared to April) and 66.24% after 4 months (compared to April).
Getting Started: Who is this talking person?
My name is Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR, and I am a Holistic SEO Expert. I work in many different fields, from front-end to Data Science, from UX to CRO. I have a fully remote agency that works with clients around the globe, which is called Holistic SEO & Digital. If you want to improve the SEO Industry and discover new methodologies, I am always open to new eager recruitment.
Today, I am gonna show you a complex Search Engine Terminology with concrete and rapid results from real-world SEO along with JetOctopus’ vision.
Introduction to Brand’s SEO Case Study: 1.200.000 Crawled Web Page by Google in a Single Day
Your web site can have a true organic reach potential but it can be melted or diluted because of the too many unnecessary, unimportant, similar, and useless URLs for the Search Engine Crawlers and Algorithms.The reason for this situation can be Site-structure, Filter Structure or Content Structure.

We will explain what Ranking Signal Dilution is and how it does harm your SEO Performance and Site Quality Score in the eyes of Search Engine. We also will discuss what the Organization of Crawl Resources is, Cost of Crawling, and Understanding Web Pages from a deeper perspective.
Our SEO Case Study and Theories will be discussed over the Biggest Sexual Health Products Producer’s website from Turkey and its shaky site migration process’ effects on the Web Entity’s Organic Search Performance.
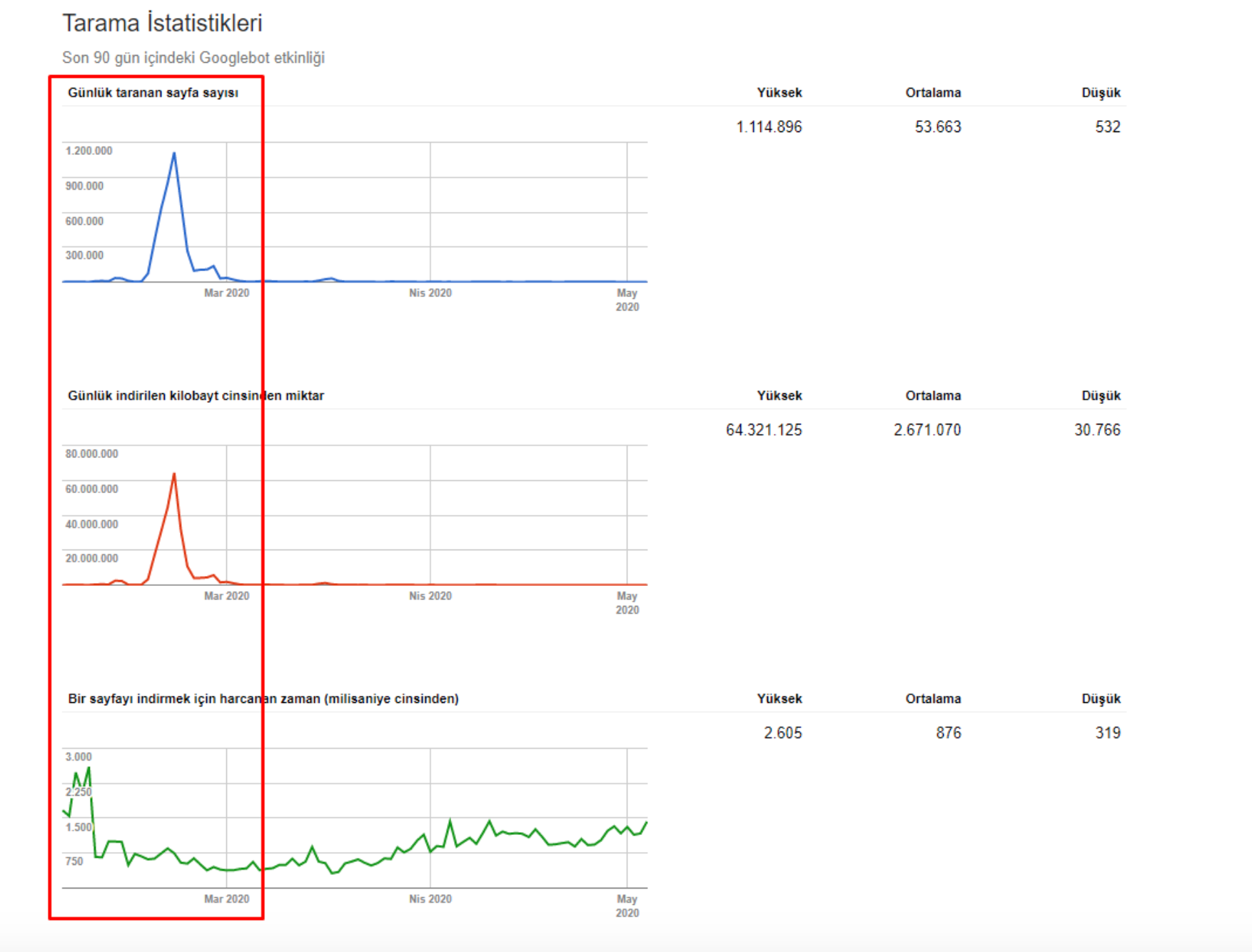
The Brand’s managers have decided to change their web site’s infrastructure and design 5 months ago.
Unfortunately, during Site Migration, there were some points not considered by either the Software Agency or the SEO Agency at that time. It was the nature, concern, and capacity of the Search Engine.
Because of the wrong URL Structure and Wrong Search Engine Communication, our Valid URL Count jumped to over 750.000 Thousand, and Excluded URL Count jumped to over 2.5 Million in a very short time.
So, how is our Organic Search Performance affected by this unnecessary URL and Category Bloating? Our Organic Traffic had decreased over %30 in 3 weeks. In this process, I wasn’t on the project. Site Migration happened in December-January, I have started to project in February.
And, I have performed the longest SEO Crawl of my life…
Before proceeding more, let’s take a look from the perspective of Search Engine to the SEO Theories.
What is the Ranking Signal Dilution?
Ranking Signal Dilution is a conflict when a Search Engine views multiple web pages from the same Web Entity for a particular Canonical Query and Canonical Intent. As a result of this conflict, the Search Engine shares the Rank Power of Web Entity in the same Knowledge Domain for the same Canonical Query and Canonical Query.

Thus, competing pages are created in the same query group. So, how is this different from Keyword Cannibalization?
Keyword Cannibalization is when two separate URLs from the same domain are related to the same query. However, this does not necessarily create a Ranking Signal Division. Webpages in Cannibalization can target different Query Intents or User Groups.
In the case of the Ranking Signal Division, there are many different pages for the same Canonical Intent-Query.
These similar pages not only create an unnecessary Crawl Cost for Search Engine but also increase the Evaluation Cost required to understand which page is more relevant to which query-intent. In other words, it creates a site bloating that is full of unnecessary pages and difficult to understand.
What are the Knowledge Domain, Canonical Intent, and Canonical Query
Let me explain the concepts of Canonical Query, Canonical Intent, and Knowledge Domain, mostly used in Google Patents.
- Canonical Query is the representative Query in the core, expressed by many queries written in different ways.
For example, Child Development, Child Growth, and Child Growth Stages, Things to be Considered in Child Growth.
- Canonical Intent, on the other hand, is the situation where many Queries written in different ways carry the same intent. There can also be multiple intents in the same Query. These are called Sub-intents.
- Knowledge Domain is the sum of Canonical Queries and Canonical Intents in a given hierarchy, within a particular system and in relation.
So, how did the brand’s web site manage to create an infinite number of copies in the same Knowledge Domain for the same Query-Intent group?
Here, at this point, we should move a little away from SEO Theories and Concepts and focus on a more practical concept, Faceted Navigations.
Faceted Navigations, Ranking Signal Division, and Crawl Efficiency
Faceted Navigation is a system that creates new web pages with filters based on options such as size, gender, type, color, date, brand, etc. for the product, service, or object, which is mostly used and searched in e-commerce sites.
Although the brand has not a very high product variety and product type (because of the industry normals), it has switched to a very detailed and not systematized Faceted Navigation structure.
This structure included condoms, lubricants, or different types of sexual health products.
Below you can see the Faceted Navigation structure, which has been developed only for an e-commerce site with 40 to 50 products in total.

What are the Positive and Negative Effects of Faceted Navigation on SEO?
- The most important benefit of Faceted Navigation is that they create web pages that can meet sub-intents that are formatted according to different features for the same product and query group.
- These web pages act as Landing Page in queries with search volume while increasing the conversion rate and amount while improving the authority of the web entity in a Knowledge Domain and its historical data.
- The disadvantage of Faceted Navigation is that when used in large numbers and uncontrolled, they create millions of similar or completely duplicate and unnecessary pages.
- At the same time, they can be ranked in different queries that may damage the image of the company, and a significant majority of them are ranked in queries that are never sought, causing the web entity to bloat.
For these reasons, Faceted Navigation must be used in a controlled manner. The user’s search habits, Thinking Pattern (Neural Nets), and query priority, the volume should be taken into consideration.
Filters that are undesirable to be scanned should be disallowed, preventing both reducing the Crawl Efficiency by creating Crawl Cost and creating unnecessary PageRank Damping.
For example, in the query for the Big Summer Red X for Women query, it is necessary to ensure that the web pages are differentiated within themselves by choosing the filters that can best meet the search intent in the semantic hierarchy and Neural Nets.
So, how was the situation in Brand’s Web Entity?
How can 40 Products and their faceted navigation create more than 3 Million URLs?
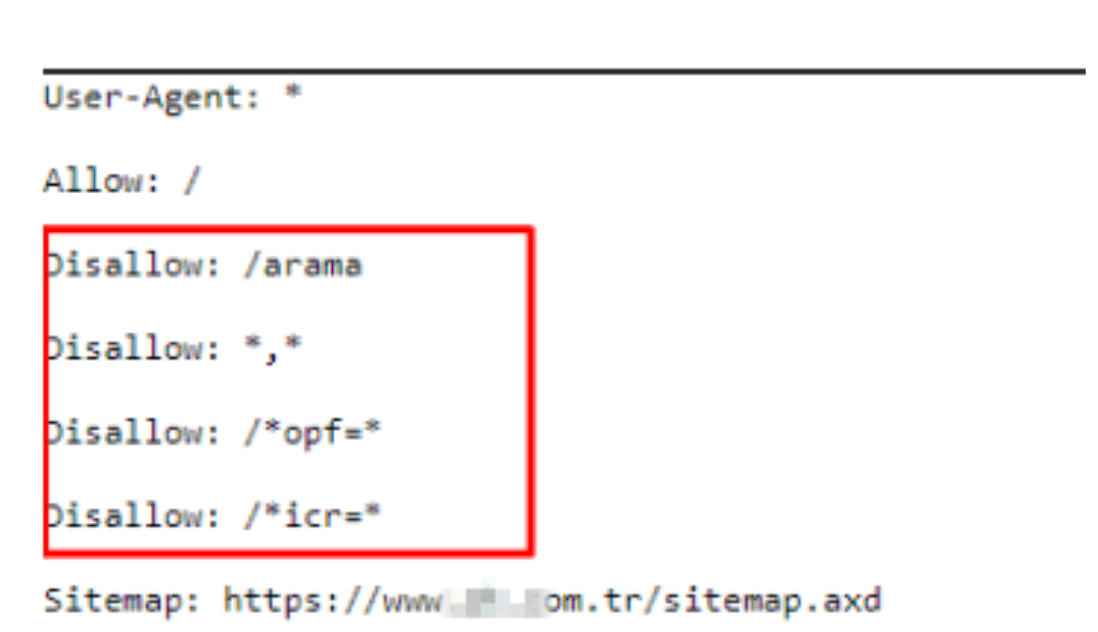
The company itself probably did not have the possibility of 40 products creating millions of URLs with faceted navigation. However, this can hardly happen, especially if you have URLs with parameters hidden from Google Search Engine. Let me introduce you to the Brand’s Robots.txt file.
Each product URL has more than one “opf =” URL in its source code for the sale of the product and the stock operations in the database.
All of these URLs are disallowed.
Below you can see some of the URLs with example “opf =”.

Filters created in total were based on the type, price, and size of the product. The total number of filters was only 25.
In this case, with 40 products, 25 filters, millions of URLs at first glance may not seem possible. However, each product page had multiple URL breaks disallowed in the background.
These disallowed web pages were the first part of the problem of this Site Migration and Faceted Navigations. If you look at the subject from the perspective of the Search Engine, we can deepen our review a little bit.
Inaccessible Web Page Amount and its Importance for the Search Engine
Imagine that a Web Entity that exists for years has a total of 150 web pages. Then, suddenly the total number of URLs of the website is increasing to exceed 3 million.
In this case, the Search Engine will first increase the Crawl Quota it allocates to the Website.
In this case, the Search Engine will expect 5 things in total and basically from Web Entity that requests more Crawl Quotas.
- Providing better and necessary content to the Search Engine User
- New web pages created are open to Search Engine Crawlers and do not tire of Crawlers
- New web pages created can be understood and evaluated by Search Engine Algorithms
- New web pages have unique aspects from rest of the Web for the Search Engine’s perspective
- In return for the new Crawl Quota created, the pages requested to be indexed contribute to the Search Engine ecosystem (I call this as Index Score.)
I always ask myself 5 topics here when creating a new web page. At the beginning of the Case Study, I said that when I took over the project, I had the longest SEO Crawl of my life.
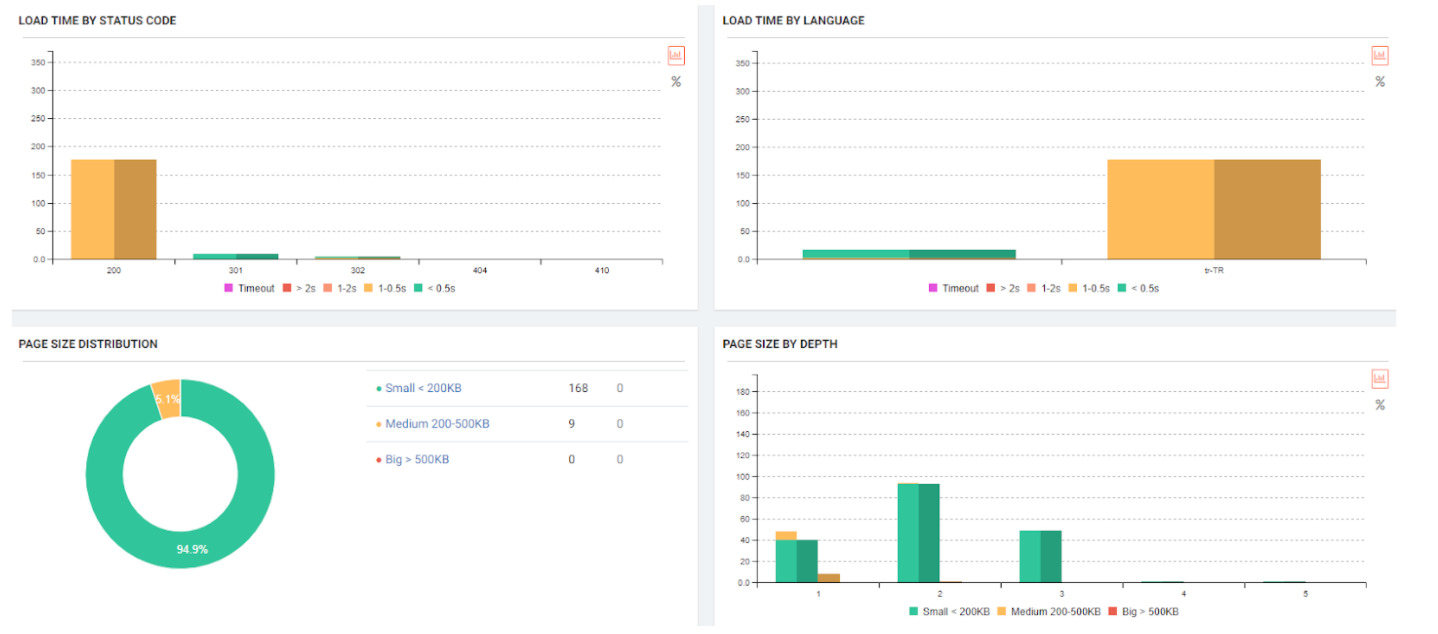
The reason for this was the endless URL Loop. By the end of 6 hours, I discovered 1.2 million URLs, but I could only crawl 555,000. This scan took 4.5 GB in total on my computer, and I consumed an internet quota over 20 GB for scanning.
Now, consider the cost of Google or Yandex? And in return, question how many of these 5 criteria are sufficiently found on newly opened web pages. Let’s continue to dive into the world of Search Engine a little more.
Overall Web Entity Metrics and Index Quality Score
Web Entity and Website are not the same things. Web Entity includes a brand’s Social Media Accounts or comments on the internet, and news from different channels.
Therefore, a Website is affected by the Overall Status of the Web Entity it is in. Index Score, as mentioned in the previous title, is the value you add to the internet for a certain browsing and crawling budget.
Even though there are similar thoughts in Search Engine Patents or Theories, the Index Score concept is not mentioned. Therefore, if you can find a better name, I agree.
If a Search Engine crawls millions of web pages from a Web Entity, it should contribute to the user and the information and function network on the Internet.
Ok, now let’s follow the example of our Case Study Subject.
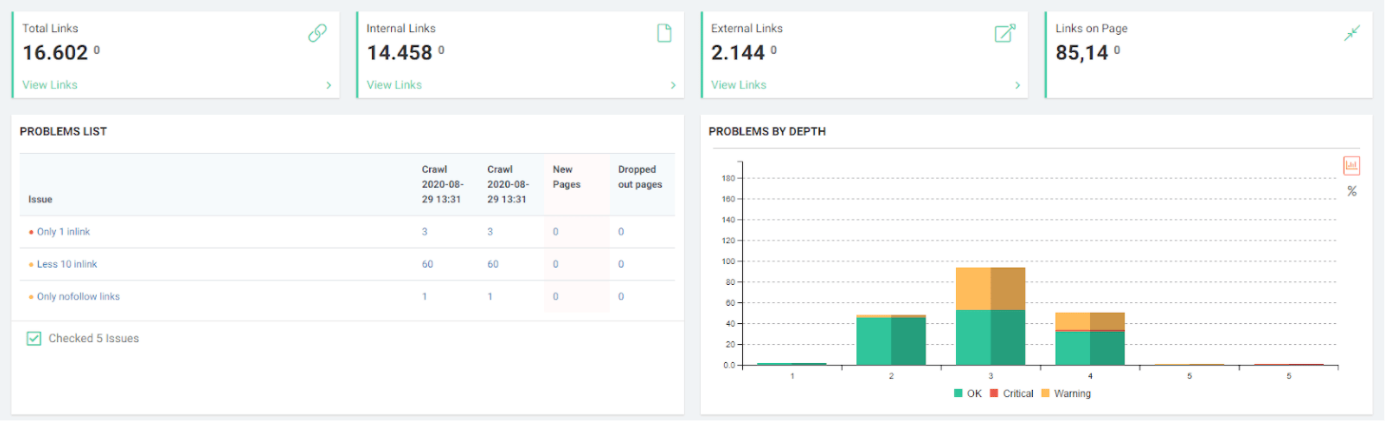
Importance of URL Structure and Effects of Uncrawlable, Unclear Webpage Domination on a Web Entity
None of the 5 criteria mentioned above were valid for new web pages created in the our Brand Web Entity.
- Most web pages could not be crawled.
- Web pages were not understandable.
- Web pages were not unique.
- Web pages did not offer any value despite the cost they created.
- Web pages did not offer the user convenience content or innovation and difference functions.
In short, these 5 questions summarizing the 23 questions that Amit Singhal asked for Core Algorithm Updates were unanswered for the Brand of our Case Study.
Well, we still haven’t told how more than 3 million URLs came up, right? We said some of it but … It still has time. First, let’s read an episode from Google’s Guideline below.
Below, you will see the transformation of Search Engine Theories, which I have explained directly with the sentences I get from Google Guideline, into practice.
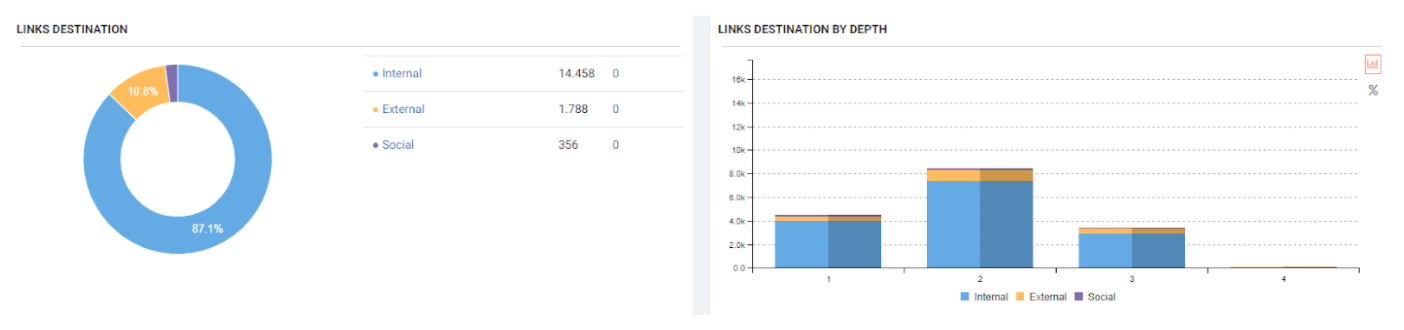
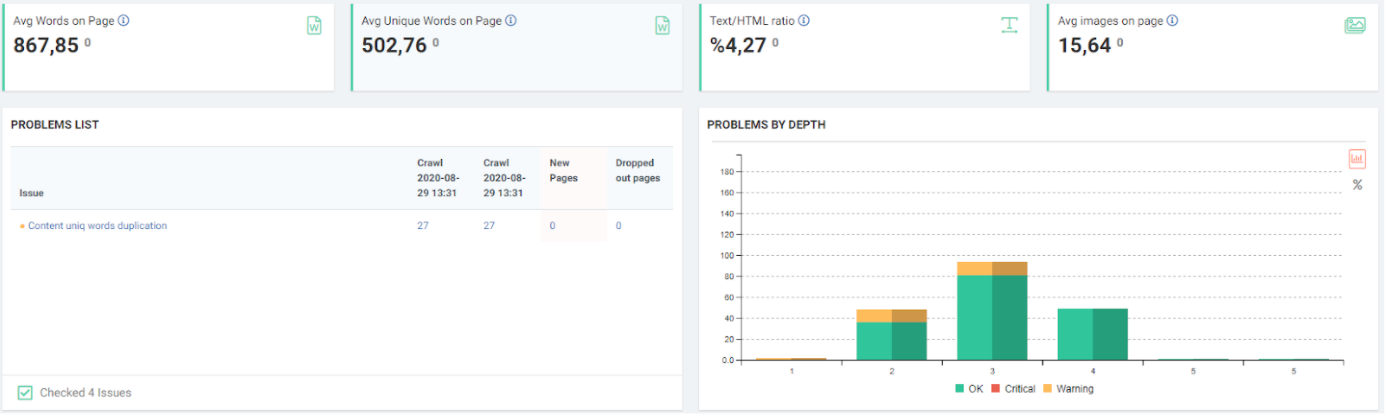
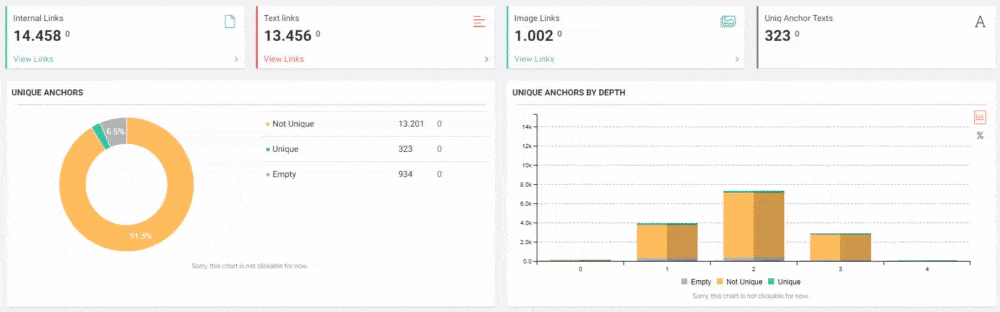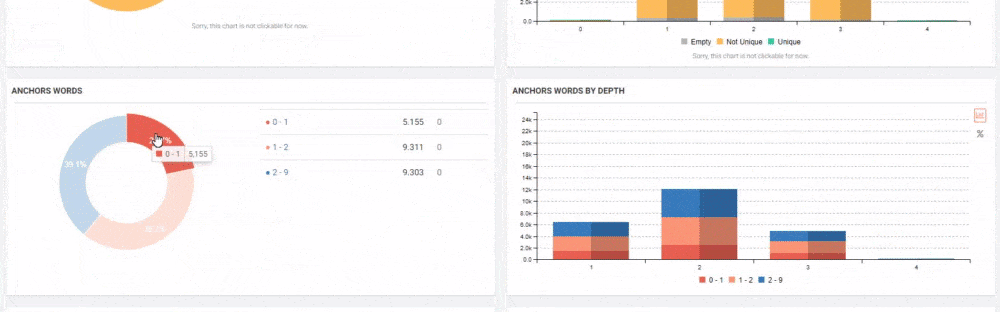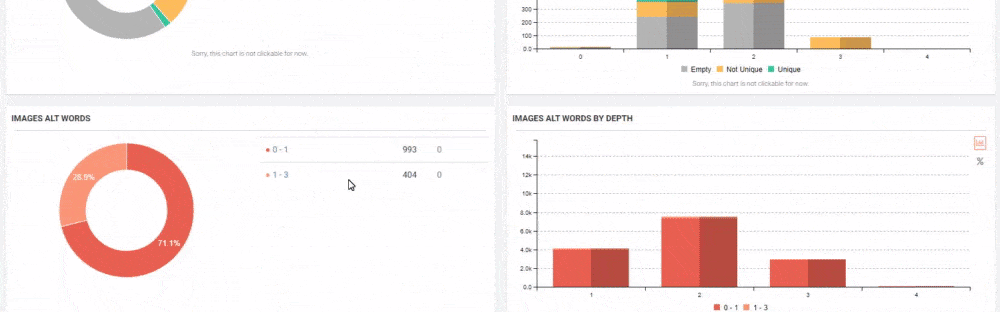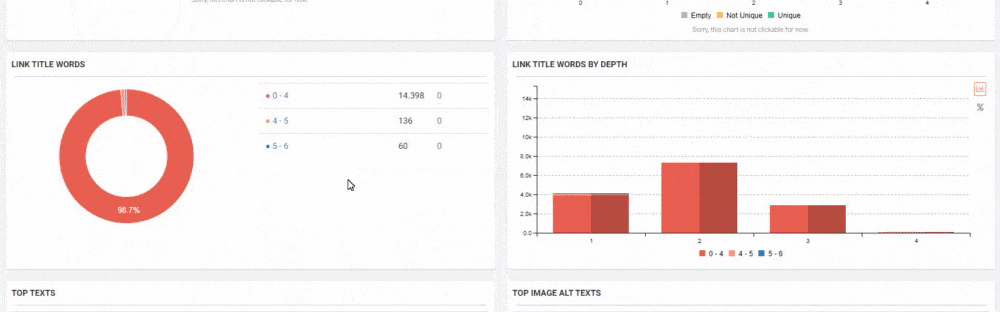
JetOctopus can classify the links in the web entity according to their “destination” and the click depth of “destinations”. Thus, you can see how many links came from which section to new content created.
Keep a simple URL structure
Overly complex URLs, especially those containing multiple parameters, can cause problems for crawlers by creating unnecessarily high numbers of URLs that point to identical or similar content on your site. As a result, Googlebot may consume much more bandwidth than necessary, or may be unable to completely index all the content on your site.
A simple and understandable URL structure can show Search Engine everything about your website in a Semantic, Hierarchical, Consistent and Holistic structure. Just by converting the sitemap of two separate web Entities into a data frame with Python and comparing them to each other, you can understand the differences between them by their URL structures.
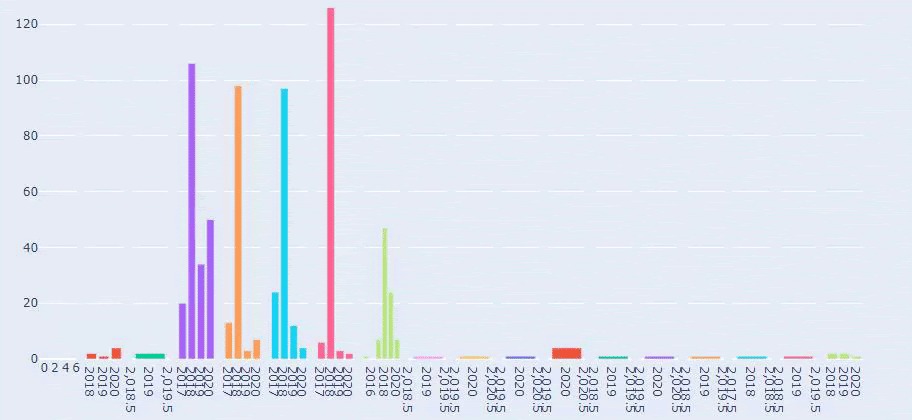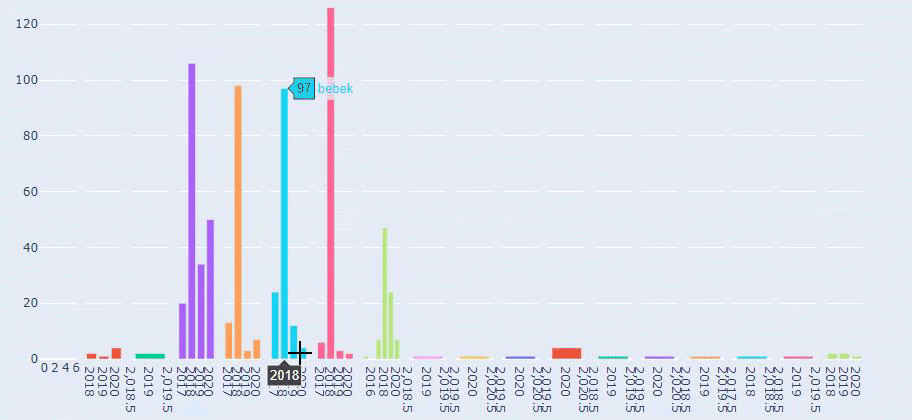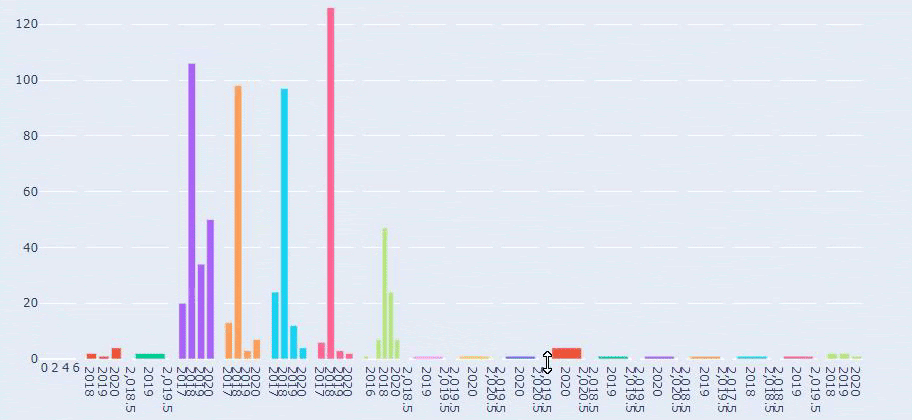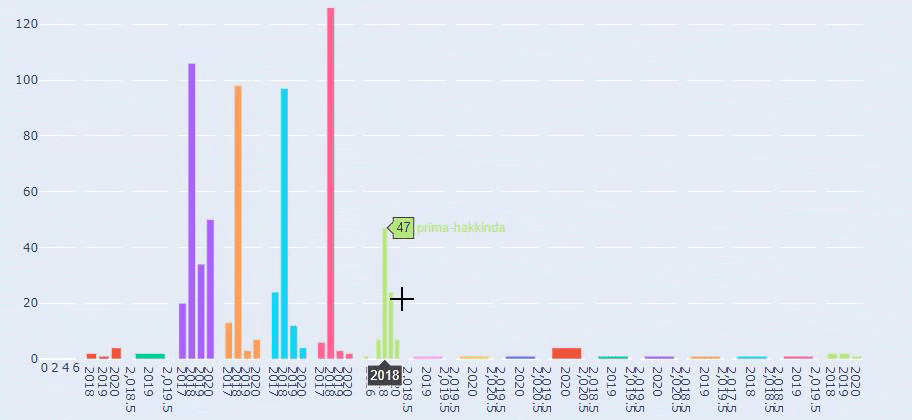
In this context, a simple URL Structure for Crawl and Evaluation Cost is important no matter the year. It is also necessary to use the same Semantic and Basic structure in your Sitemap Index file or in your Social Network, content or even in your Semantic HTML to communicate better with Search Engine.
Let’s move on to the second part.
URL Ranking Signal Division and Ranking Signal Consolidation
To consolidate link signals for similar or duplicate pages. It helps search engines to be able to consolidate the information they have for the individual URLs (such as links to them) into a single, preferred URL. This means that links from other sites to http://example.com/dresses/cocktail?gclid=ABCD get consolidated with links to https://www.example.com/dresses/green/greendress.html.
If you don’t explicitly tell Google which URL is canonical, Google will make the choice for you, or might consider them both of equal weight, which might lead to unwanted behavior
To avoid spending crawling time on duplicate pages. You want Googlebot to get the most out of your site, so it’s better for it to spend time crawling new (or updated) pages on your site, rather than crawling the desktop and mobile versions of the same pages.
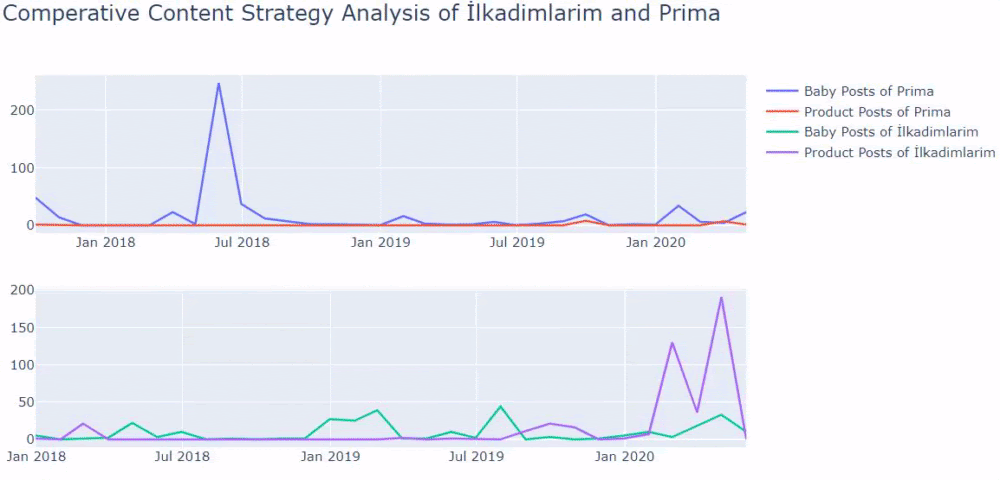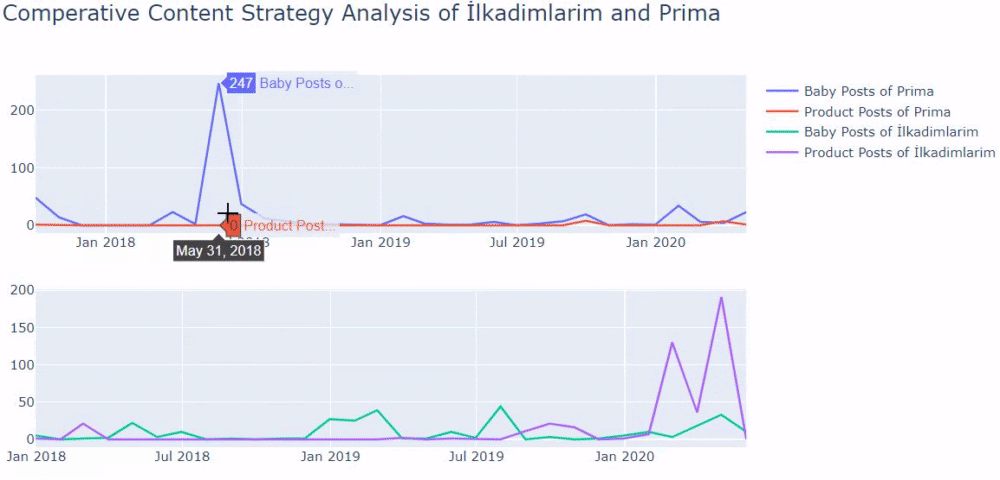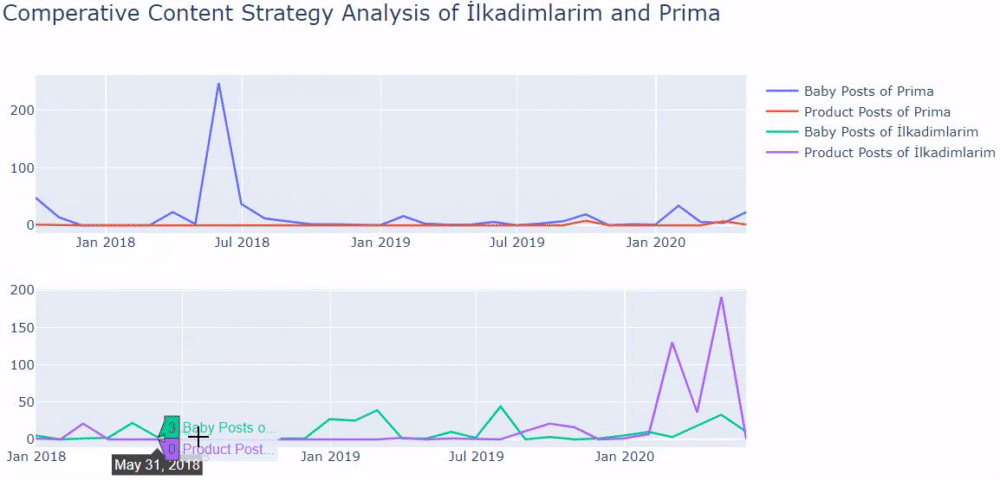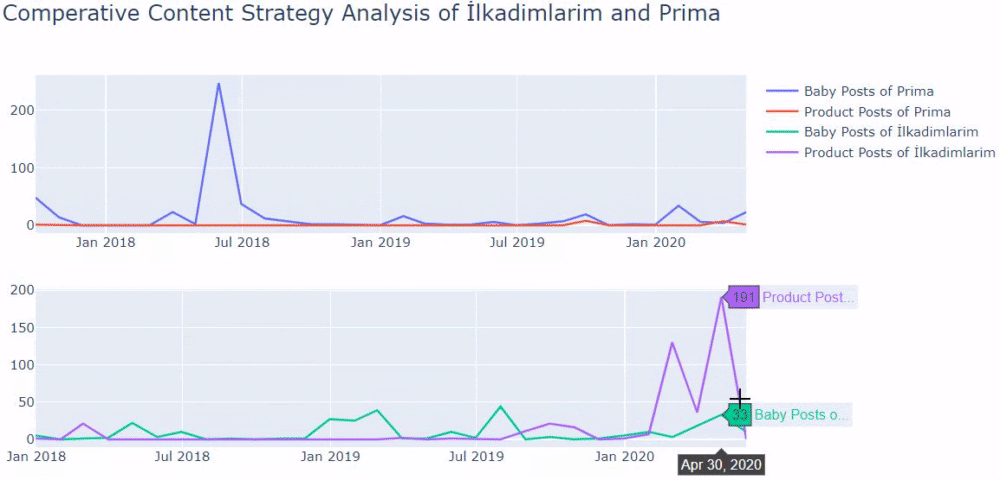
Two related quotes in Google Guideline also explain the effect of concepts such as Ranking Signal Division and URL Structure. It is stated that the same pages should be consolidated with the “canonical” tag of Ranking Signal Effect, while it is stated that it should be given clear messages to the Search Engine with a simple URL structure.
Now let’s observe the situation we experienced in the Case Brand’s Web Entity if you want.
Sudden Effects of Web Entity Bloating without Clearity and Consolidation of URLs
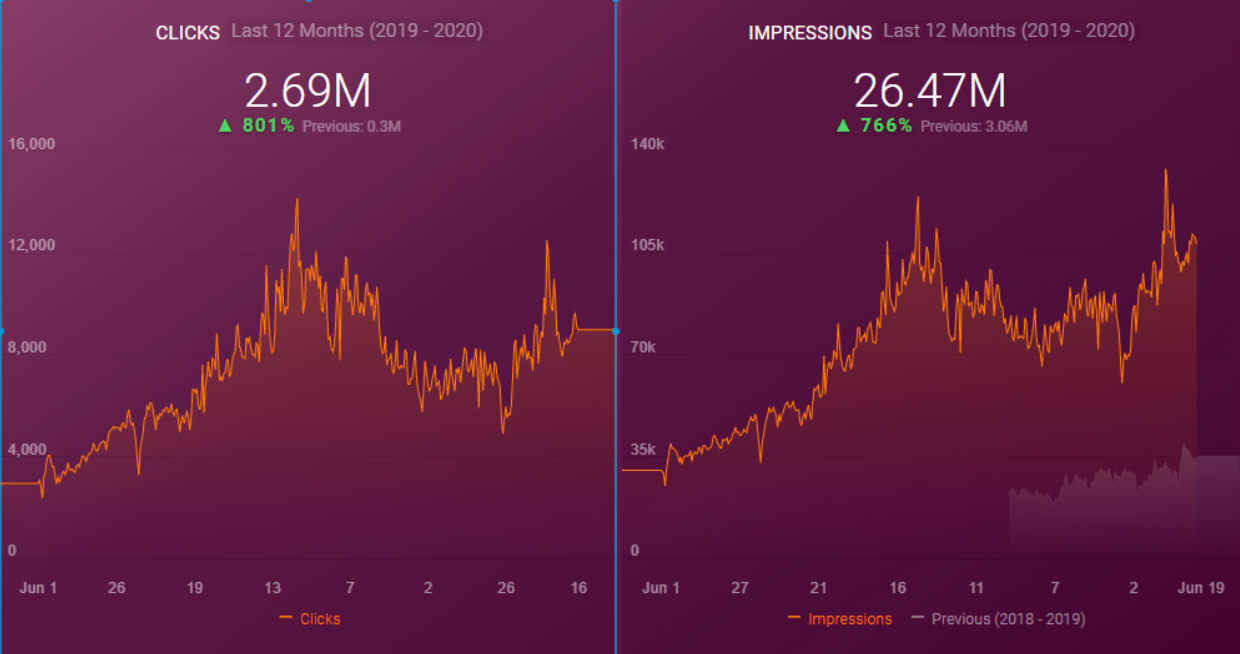
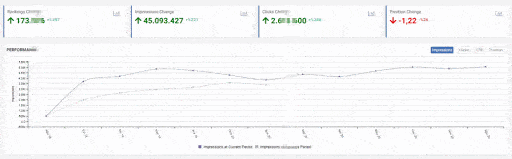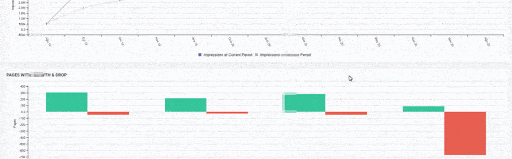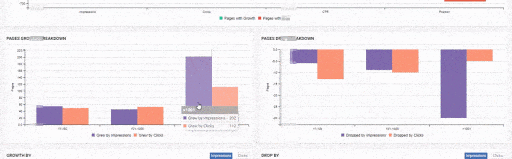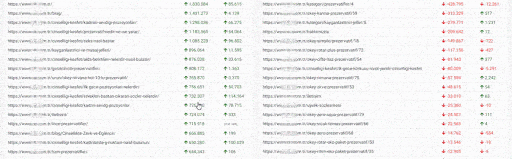
When we show the last 12 months of Click Data at the beginning of Case Study, you can remember the fall in site transition from January onwards.
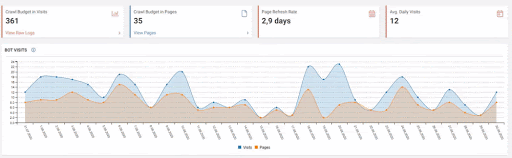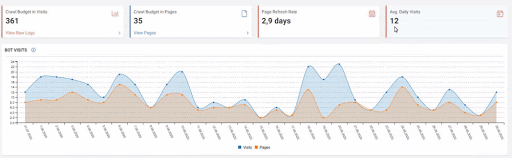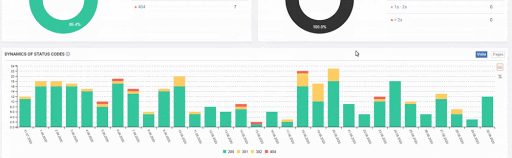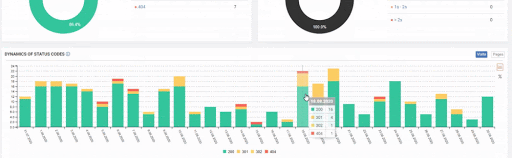
Below you will see the data of Click, Impression and Crawl Stats, with the same period mark-up.
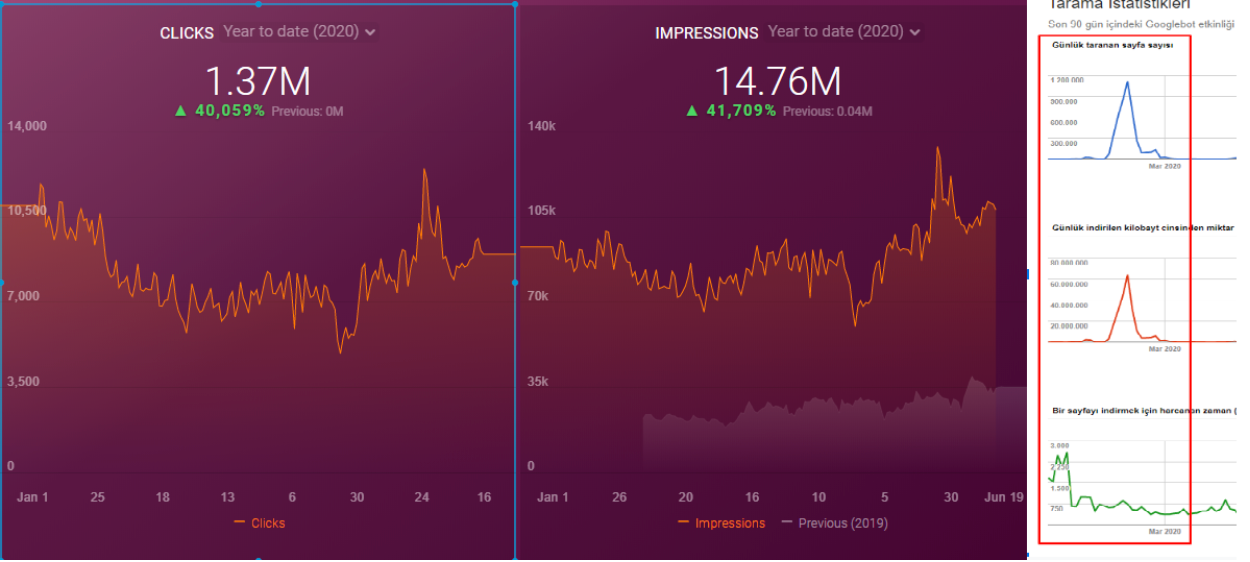
When we put Crawl Stats next to this graphic, which resembles the shape of the arc, the following results appear.
- Googlebot has detected a change and therefore increased the Crawl Quota.
- Although it has more than 3 million URLs, it has ceased to crawl or fetch around 1,200,000 more URLs.
- Thus, Google Algorithms have stopped spending resources, seeing that the new URLs that have been created are largely meaningless.
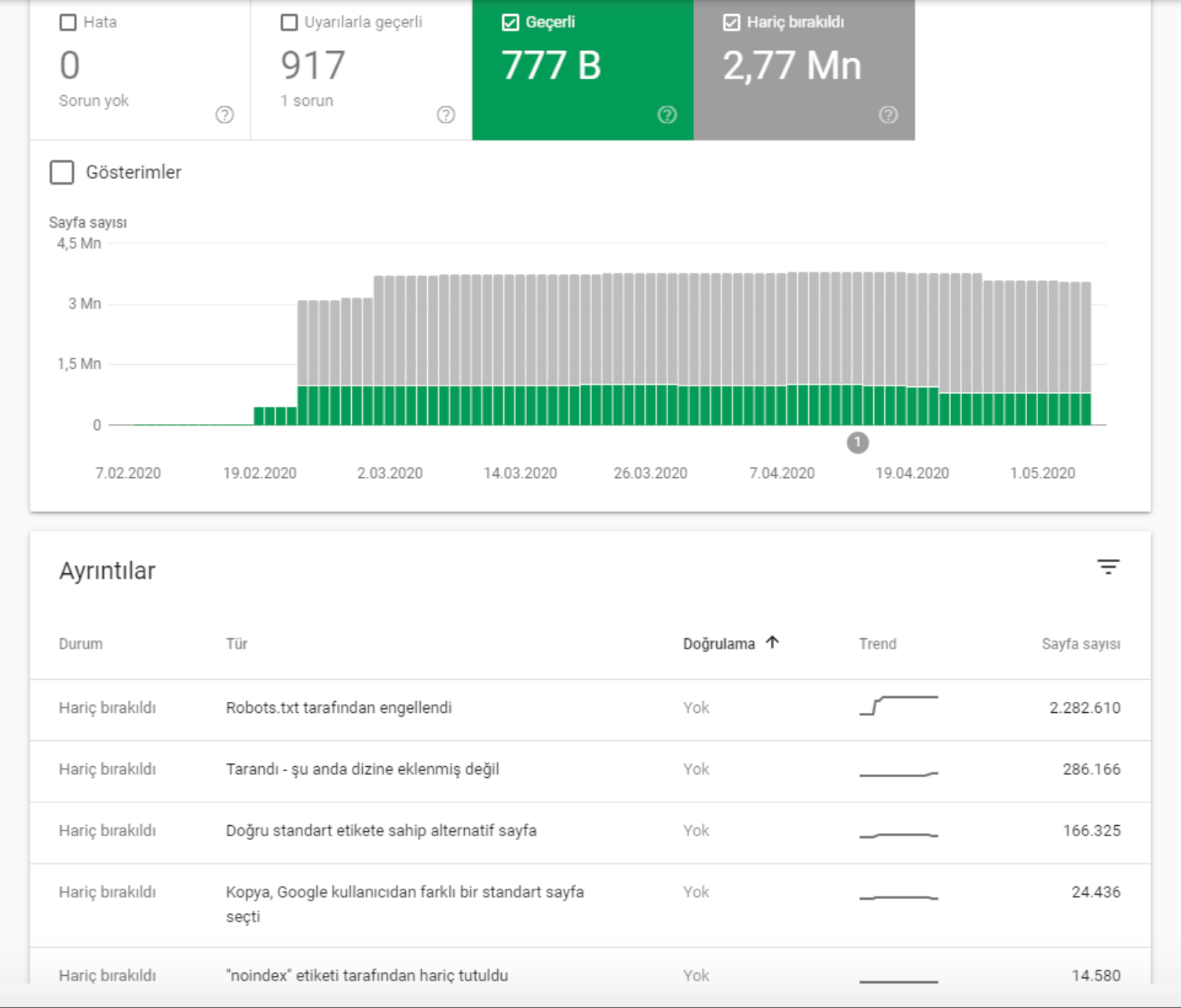
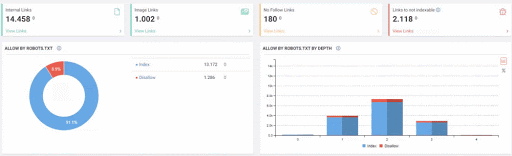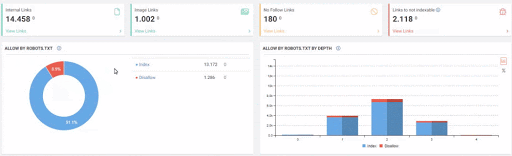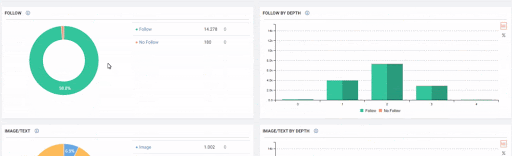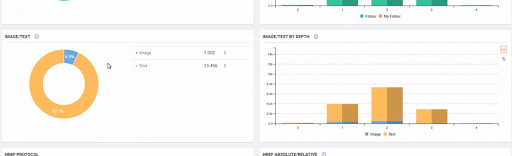
- As it appears in the Coverage Report we shared, a significant portion of the URLs were blocked by Robots.txt, in other words 40% of Web Entity was closed to Search Engine.
- The URLs Weren’t Consolidated, They were Copies of Each Other.
- In 80% of copy pages created with uncontrolled Faceted Navigation, there was only 1 product or no product.
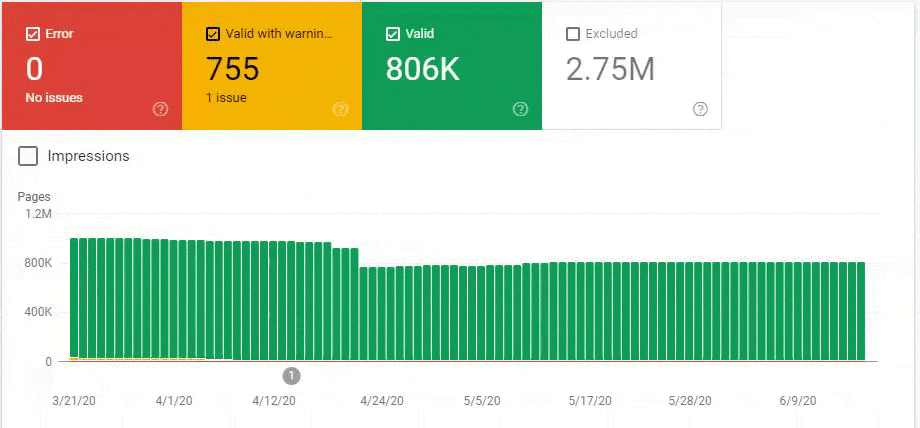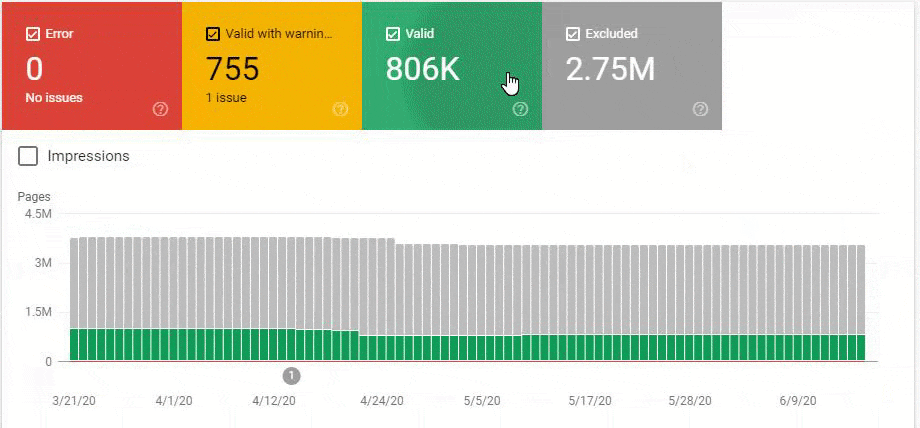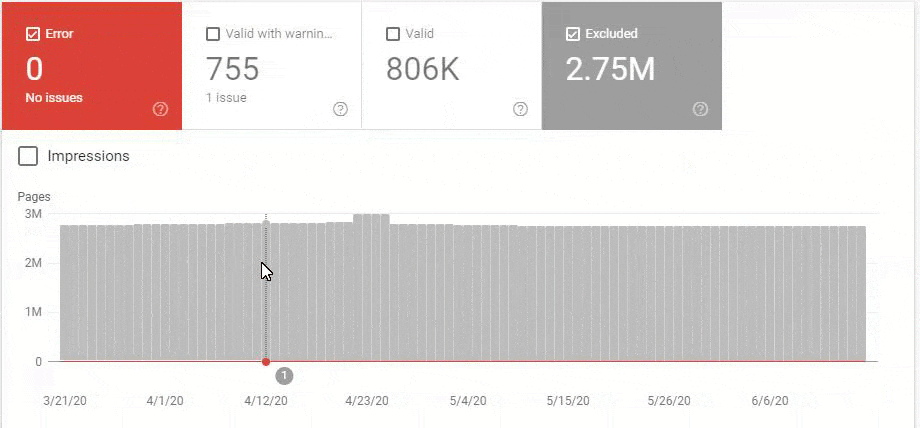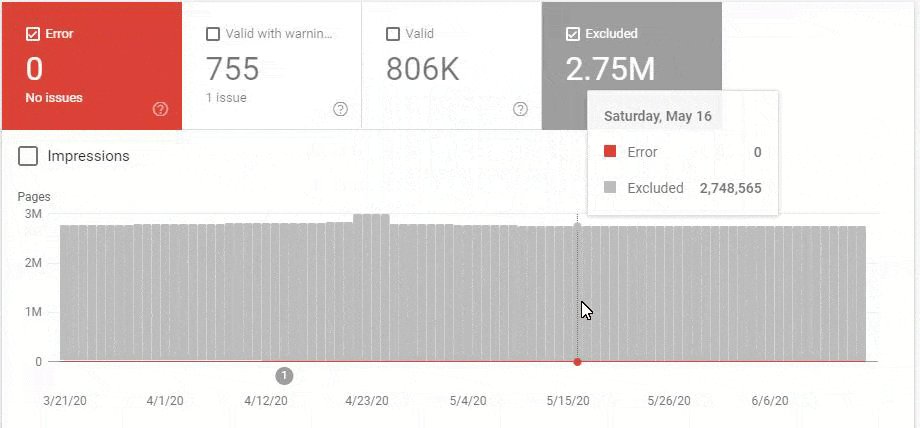
- The number of Valid Web Pages exceeded 800,000, and the number of Excluded URLs was 2,500,000.
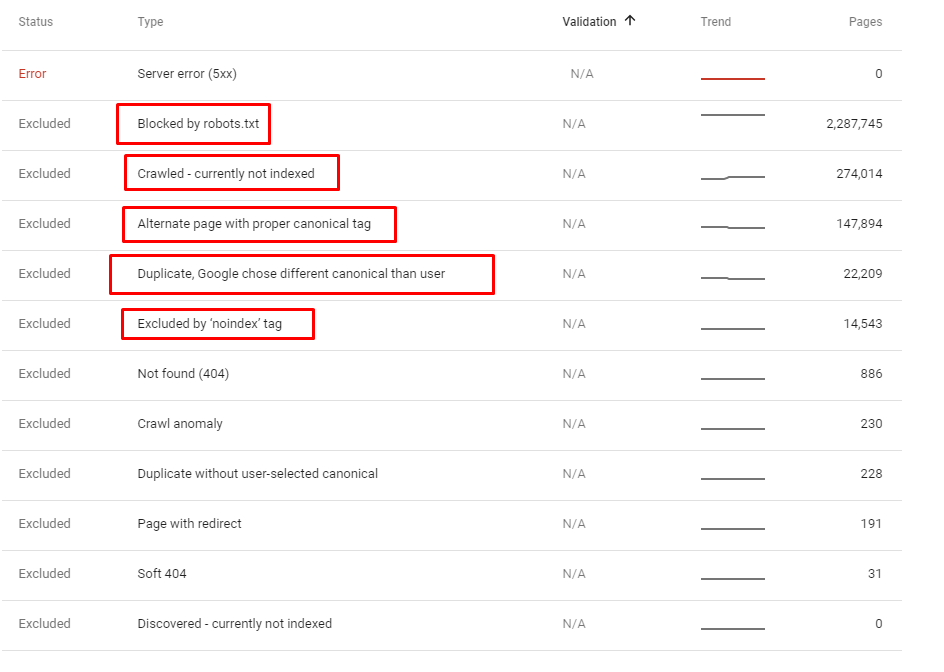
In the image above, we see that a total of 2,200,000 URLs are blocked by robots.txt. Now, let’s read another piece from Google Guideline.
Consolidation Methodologies for the Web Pages Bloating in a Web Entity
Google does not recommend blocking crawler access to duplicate content on your website, whether with a robots.txt file or other methods. If search engines can’t crawl pages with duplicate content, they can’t automatically detect that these URLs point to the same content and will therefore effectively have to treat them as separate, unique pages. A better solution is to allow search engines to crawl these URLs, but mark them as duplicates by using the rel=”canonical” link element, the URL parameter handling tool, or 301 redirects. In cases where duplicate content leads to us crawling too much of your website, you can also adjust the crawl rate setting in the Search Console.
I recommend that you always read Google, Bing and Yandex Search Engine Guidelines together. You can deepen your SEO Perspective by seeing both different perspectives on the same problems and different degrees of information on different topics.
Thus, because Google could not crawl over 2,200,000 web pages in any way, he could not understand whether these pages were duplicates, and had to treat each of them as a separate, unreliable and unique page.
Other suggestions from Google Search Engine at this point for the full processing of the subject are as follows:
- 301 Redirects: It transfers Canonical Effect and PageRank value, removes it from Index and provides better evaluation of Crawl Resource.
- Being Consistent: Use consistent URL Structure, Site Categorization, and Internal Link. Don’t link different web pages from different pages without context and use the same link for the same content/context.
- Top-level Domain Usage: You may use country-top level domain for showing relevant content for a different country. But, I don’t recommend this method, with a consistent and clear Site Structure, we can consolidate our Domain and Knowledge Domain Authority on a single web entity.
- Syndicate Carefully: If there is any similar or the same content over the surfaces of the web from your web entity, be sure that they mention you or link back to you so that the Search Engine can understand the original source of this content. This also can be called Link Inversion but it is a topic for another Case Study.
- Minimize Boilerplate Repetition: Boilerplate Content’s getting ahead of Main Content makes it difficult to spot Main Content, and it also prevents the understanding of what the page is about. It also increases the likelihood that web pages in the web entity will appear in duplicate. It is therefore useful to use a differentiated boilerplate for different categories.
- Don’t use stubs: Do not create blank pages for very small functions and topics.
- Control your CMS: Make sure your CMS Panel does not automatically create unnecessary and similar pages.
- Minimize Similar Content: Reduce similar page rate on web pages. At this point, I should mention that Search Engines divide the content into three as Ads, Main Content, Supplementary Content. Each page should serve a topic and link a similar topic or subtopic from the Supplementary Part.
Also, I prefer separate Duplicate Content from Repetitive Content in SEO Terminology but we see that Google doesn’t prefer doing that. Also, this is the topic of another day.
Now, with your permission, let’s move on to the conclusion section by sharing the Valid URL Profile of the Brand of our SEO Project, explaining the true cause and content of URL Bloating.
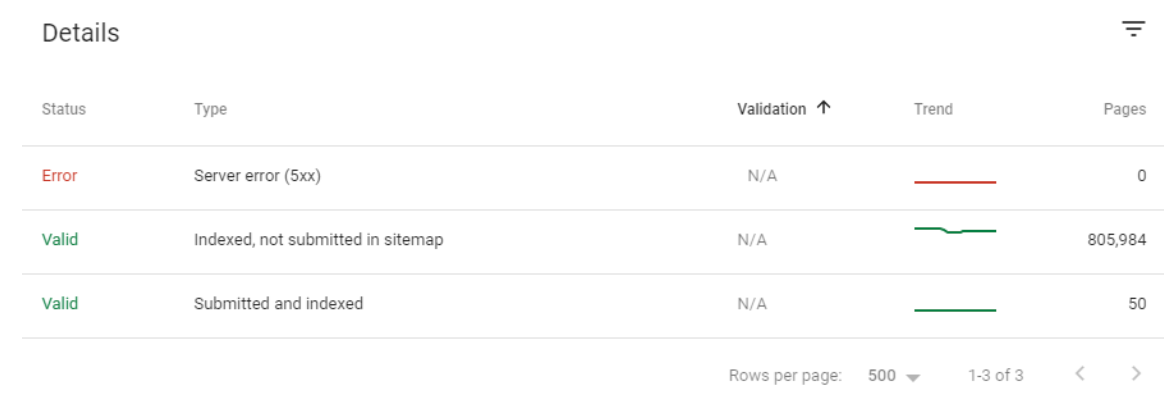
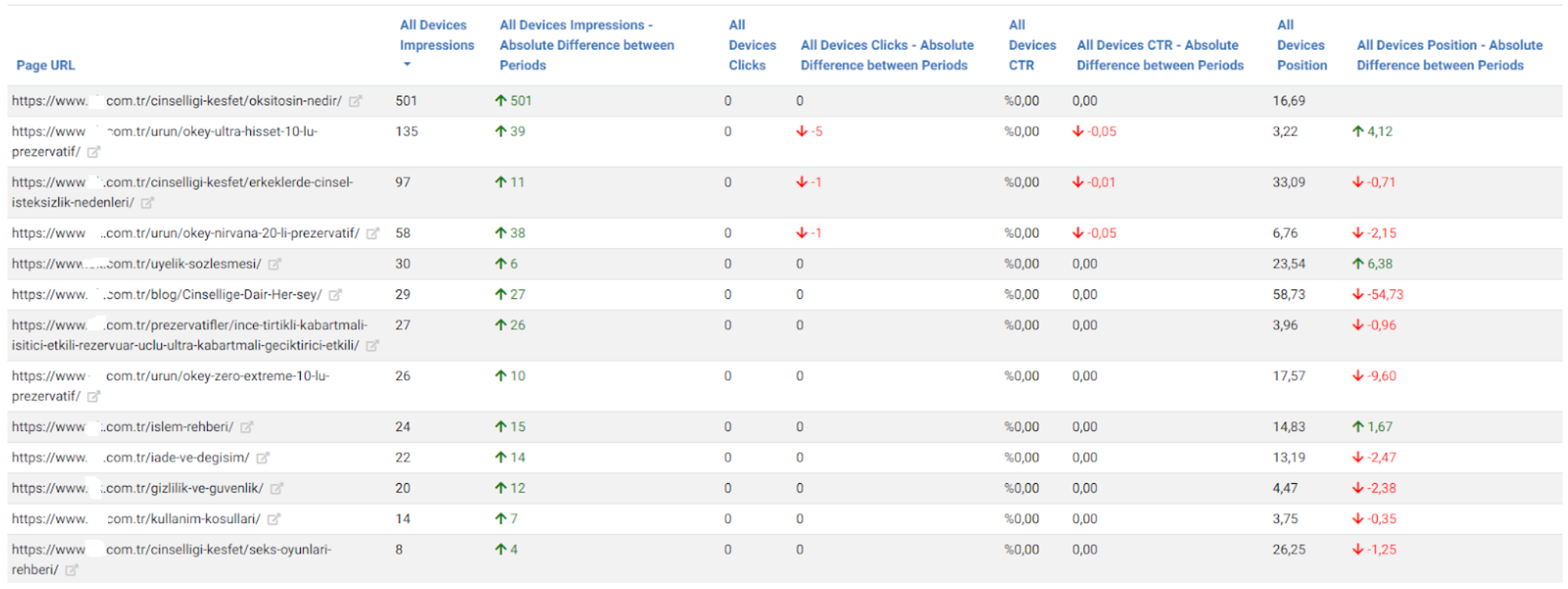
We see here another error. None of these newly created URLs were in the sitemap. Below, you will see a slice from this unnecessary URL ocean with the last crawl dates and URL Structure.

Let me translate the URL structure here for you.
- It says that this URL Contains Prezervatif Products which are jelly and non-jelly, transparent and non-transparent, fine tip, and flavored.
- The second marked URL says that this web page only for the preservative products which are retardant, ultra-thin, embossed, serrated, and unembossed.
- The third one is for the preservatives which are latex, flavored, non-flavored, heater, extra thin, extra embossing, orgazmax gel, tight, extra lubricant.
And also the content of these web pages naturally are thin, duplicated, or empty.
We said before that there were 25 different filters for three different aspects such as price, feature, and size.
Each filter was able to create URL variations that were repeated and unreasonable. So, we seemed to take the factorial of 40×25, unnecessarily and pointlessly.
At the beginning of the Case, we shared an image with the numerical data of the Coverage Report.

At this point, you can see that Googlebot sees millions of URLs that cannot be separated from each other according to Query-intent groups, which are unnecessary, irrational and meaningless, duplicate, or rather empty, neither content nor explanation nor targeted.
Ranking Signal Division for Excluded-Blocked by Robots.txt URLs
At this point, we must include URLs blocked by Robots.txt in URLs that create Ranking Signal Dilution. This is because Google understands sections of a website with the help of URL Structure. Even if the content of these URLs is closed to Google, the structure in the URL is not closed.
The only difference of these URLs from those open to crawl is the “opf =” parameter. As such, Google will not be able to consolidate a URL it cannot reach, and will see them as separate pages, as noted in Google Guideline, with similarity to what they can crawl.
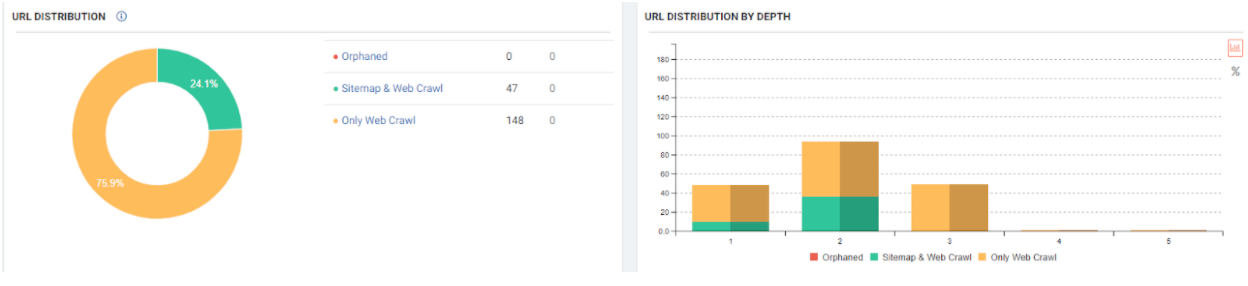
In other words, URLs with “opf =” whose content cannot be seen and whose content is 99% the same, here also created the Ranking Signal Dilution. Also, the prediction here is correct. Any URL with “opf =” is not different from without “opf =” you version.
We see that Search Engine Concepts are in consistency.
After creating millions of similar and same pages, we can talk about how this problem can be solved, the ranking and organic traffic change, quantity, and timing after the solution.
How to Consolidate Millions of Unnecessary URLs with The Most Correct Way for the Best Search Engine Communication
Search Engine Communication is also a term from my vision. Every move you have made creates a signal in the eyes of Search Engine and carries a meaning to its algorithm. If you have a Semantic, Hierarchic, Stable, and Consistent movement for a long time, you can create a communication with the Search Engine Algorithms and their internal hierarchy.
So how to clear the wrong messages which we have sent to the Search Engines during this site and design migration? Let me explain another principle for Search Engines, it is Uncertainty and Disambiguation.
Uncertainty Principle and Disambiguation Algorithms of Search Engines
As the search engines develop algorithms and collect historical data, they can incorporate small differences or fragments into ranking systems with consistency. The effect of the little things accumulated over time and their consistency allows Search Engine Algorithms to focus their attention on the coherence of small factors from one of the easy to manipulate large factors.
The Entity-based Search Engine design that can understand the real world by saying “Things not Strings” by Amit Singhal also comes from this whole idea.
In other words, we can ask this. Why were only 35% organic traffic lost, despite millions of useless and pointless URLs reducing the Crawl and Evaluation Efficiency by creating Ranking Signal Division (Dilution)?
This is because Google knows that the content publisher has made an error. Every mistake you make or every step you take creates a Communication between you and Search Engine.
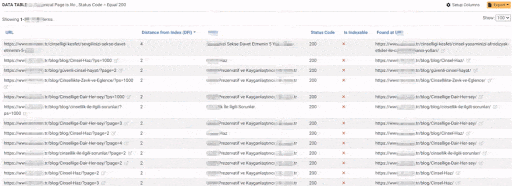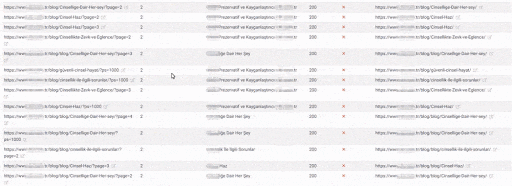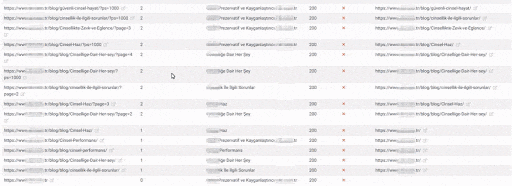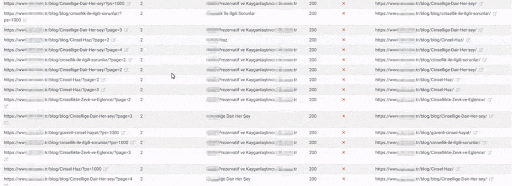
The Quality Score and Web Entity Authority that Search Engine devoted to you in Historical Data and Knowledge Domain will better protect you from the severity of such errors.
If you had made the same mistake in 2015 on Google, it would probably have lost more than 300% due to the Uncertainty Principle and Disambiguation Algorithms that day.
Today, even if millions of URLs created in a day create Ranking Signal Dilution and Crawl Resource Wasting, they did not eliminate the benefits of URLs that carry the real authority that users visited for a very long time.
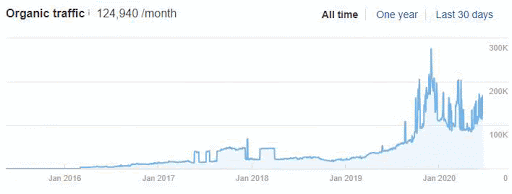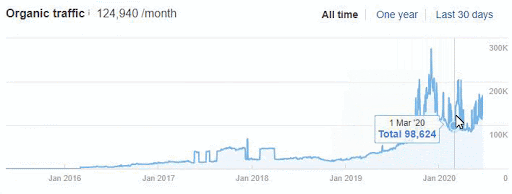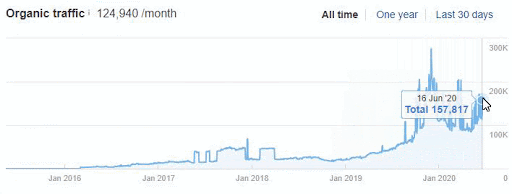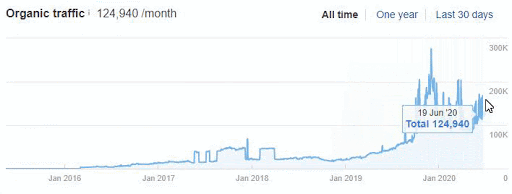
Therefore, even if Google reduced the Ranking Signals and Equity of these URLs, it did not perceive Web Entity as a complete mess.
What Other SEO Elements Are Affected by the Uncertainty Principle and Disambiguation Algorithms?
- HTML Lang Tag: Google has stopped accepting the HTML Lang Tag as it is in every Web Entity, as the content is in another language while typing “en” in the HTML Tag of each website it encounters.
- Canonical Tag: Google decided to choose which page was original because it was making SERP worse for publishers to mislead Google with their mistakes.
- Pagination: Google has stopped considering number patterns at the end of the URL or Link rel prev-next tags. He left the final decision back to his own algorithm because most people were manipulating Search Engine, knowingly or unknowingly, even if they couldn’t use it properly.
- Nofollow Tag: Google has transformed its Nofollow Tag from being a command to become a hint in order to better understand the links with the use of nofollow for everyone else.
- International Targeting: Since many people misused International Targeting in Search Console, Google started showing content to Searcher if content was relevant despite the targeted region.
- Heading Tags: Since many web entities use Heading tags incorrectly, Google has started to make decisions based on the sites it has examined the correct structure.
All these factors have one thing in common. They all can be changed quickly, used non-correctly or being spoiled.
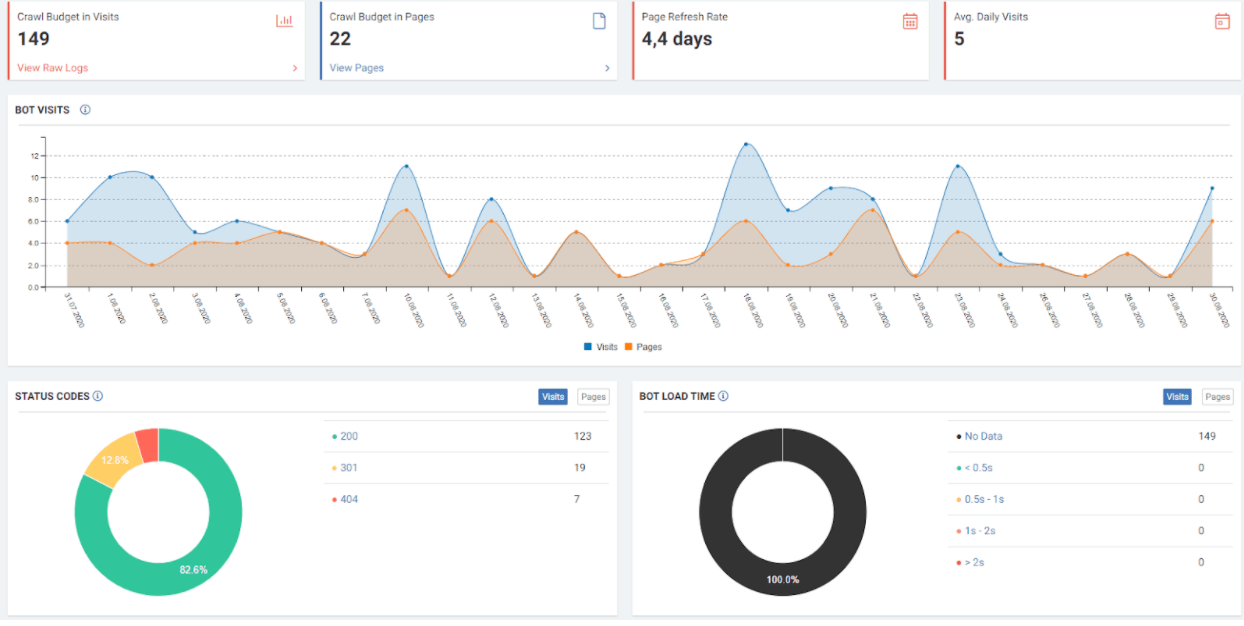
The more accurately a Web Entity communicates with the Search Engine, the Search Engine uses its algorithms most cost-effectively to understand that Web Entity. Therefore, an SEO Element not considered in another Web Entity can be used by Google or another Search Engine, thanks to your consistent and understandable structure.
“The more consistent and Semantic Code structure you have, the less guessing Googlebot will be.”
Martin Splitt,
Search Engine Journal, 2020
With these concepts, how did we recover a website that does not seem to need to be crawled by Google in 30 days after 90% of it has been scanned once and does not even offer a value to the scan?
Consolidation Methodologies for the Web Pages Bloating in a Web Entity
There were basically 4 different methods to solve this problem. In order to implement these 4 methods, the site URL structure had to be changed first.
- I stated that a web entity with only 40 products does not need any filter structure, especially if it sells sexual health products.
- I have searched the user’s neural network and their query-intent network for the best product category names and internal link structure.
- I have created a new category and product hierarchy according to Search Volume and Context.
- You can see it below, it basically includes main product queries and kinds for different intents. I have removed all of the filters so that they can be the only candidates for these query-intent groups.
- Also, I changed the content and the name of the page but I didn’t change the URL. Since we will change the entire site existence, I didn’t want to confuse Search Engines’ mind more.
- If we delete a web page with an important amount of Historical Data to just change its name along with URL, it can affect the relevance and confidence of that redirected page for the same query group since it is a completely new web page.
- Especially if you are about to delete more than 3.000.000 URLs. Also, I don’t go deep into PageRank systems here. According to Google, 301 Redirection doesn’t cause any PageRank (Garry Illyes’ Explanation) loss, but this explanation is old and also, I love to be cautious against any Search Engine’s declarations (Matt Cutts said that there is a %15 PageRank loss for every 301 redirects at the old times).
Thus, millions of URLs that I symbolized as 25×40 Factorial had fallen to 47, in the form of only 7 + 40.
So, what will happen to all of the old URLs? When the Search Engine can’t see them, what would it think? %99 of the web entity is deleted in one day? Will it stop crawling them?
No, it won’t stop crawling them. Googlebot has a really long memory. Even if you have deleted a web page, it can still crawl the same web page for the next 5 years.
Luckily, I didn’t have Log Analysis for this brand, so I need to apply mt Theoretical Information again.
Böylece bahsettiğim 4 ayrı metodolojiyi açıklayarak sonuca odaklanabiliriz:
- Use 301 Redirects with simple rules to consolidate all of the old URLs.
- Use 410 Status Code to show that all of the Valid and Excluded Web Pages are gone permanently.
- Use the 404 Status Code to leave the conclusion to Search Engine’s Algorithms.
- Use 301 Redirects before deleting the URLs, then delete the old URLs, clean the internal links, and start a validation fix via Search Console.
The sequence of all these methods from good to bad is in the form of 4,1,2,3.
Practical Process of URL Consolidation and Importance of IT Relations
We are now at the point where we had to apply the 3rd one of these methods.
The main reason for this was that the software team, another outsource resource the company was working on, did not follow the brief given as it should be.
The new URL Structure was released without notice. Thus, millions of URLs dropped to 404 without writing 301 Redirection Rules. If they are 404, you can’t redirect them to any different URLs according to Search Engine Guidelines.
404 URL means that the URL is an error or missing. We can’t redirect an error to a valid web page. I have chosen the other option, using the 410 Status Code for stating that these URLs are gone.
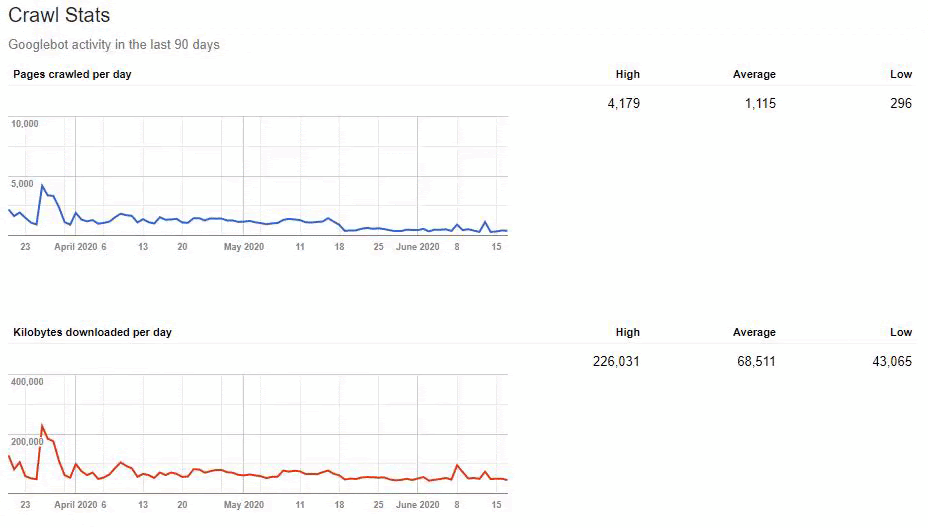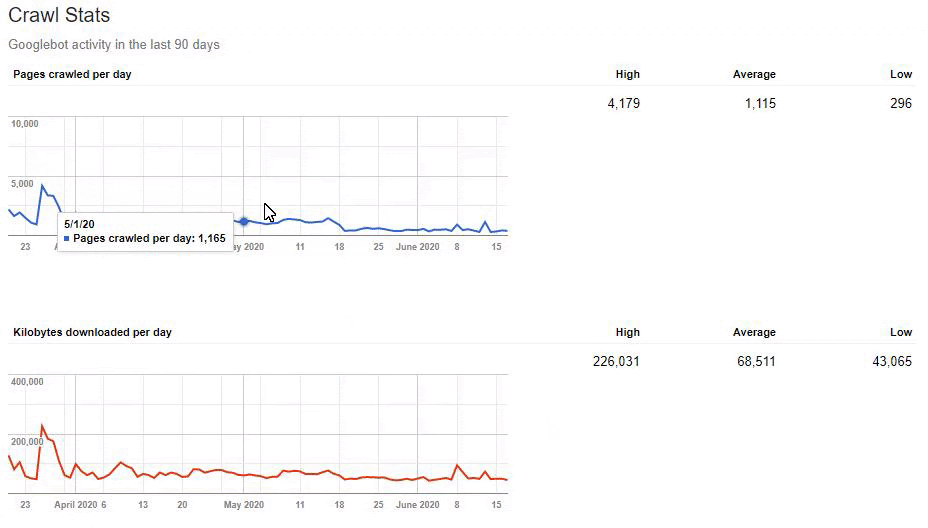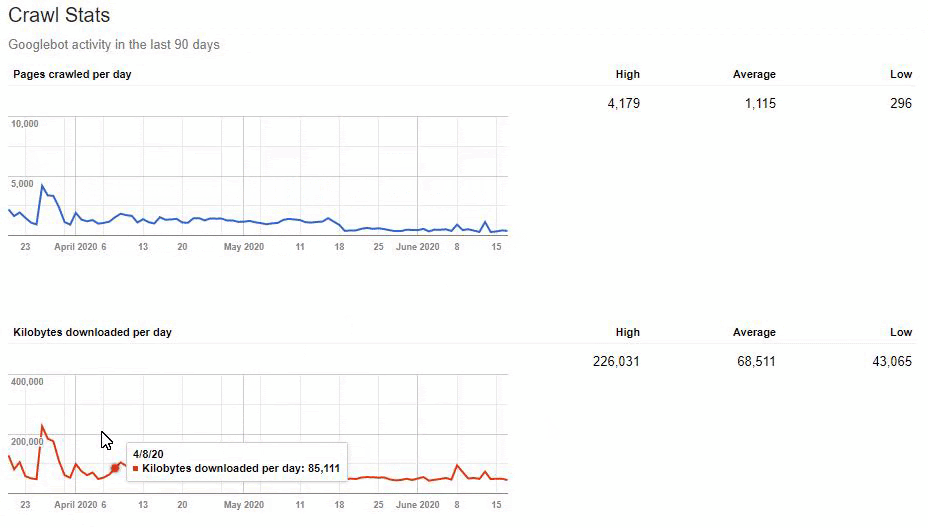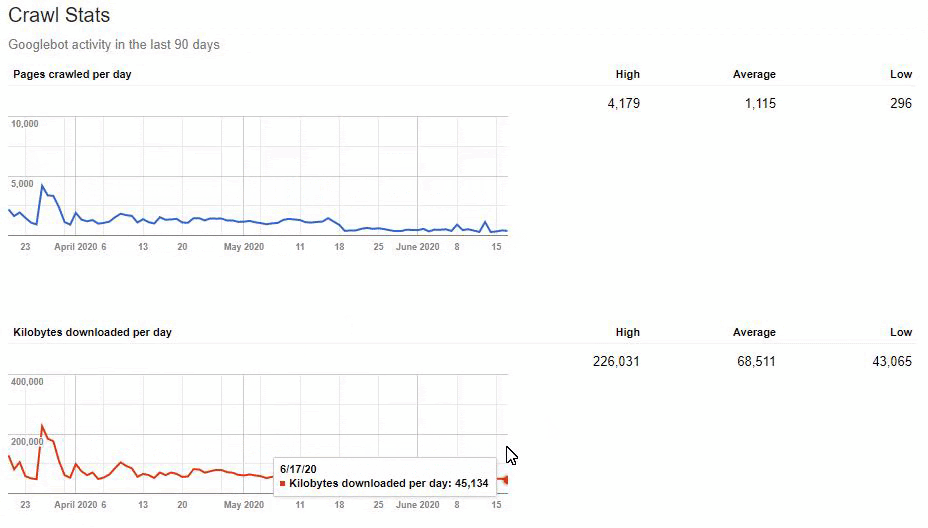
But since, it is taking time to write URL Rules to state that which are 410 and which are not. Because of this situation, I have given a sample URL Portion which consists of more than 400.000 URLs to the IT to create a URL Rule.
While they are performing 410 Status Code URL Rules, I didn’t start to Google Search Console validation. So, for now, the Search Engine is figuring out what did happen to these URLs while we are also preparing a healthy signal for its algorithms by itself.
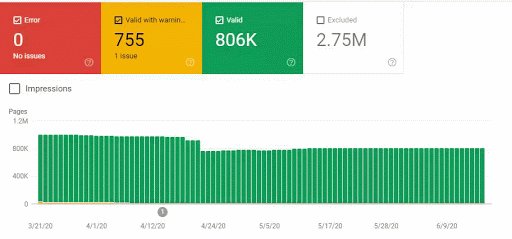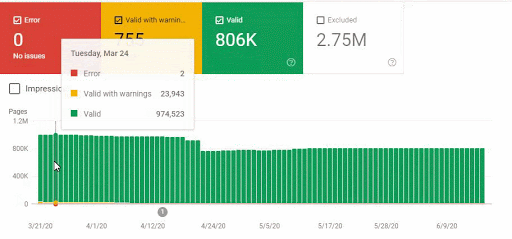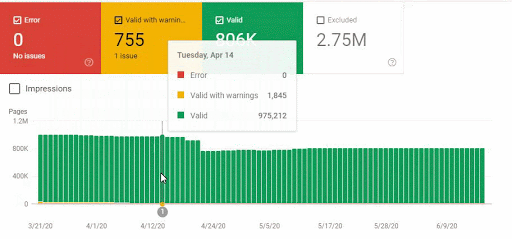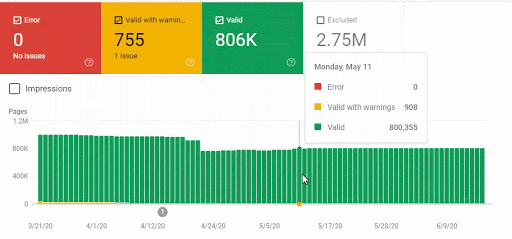
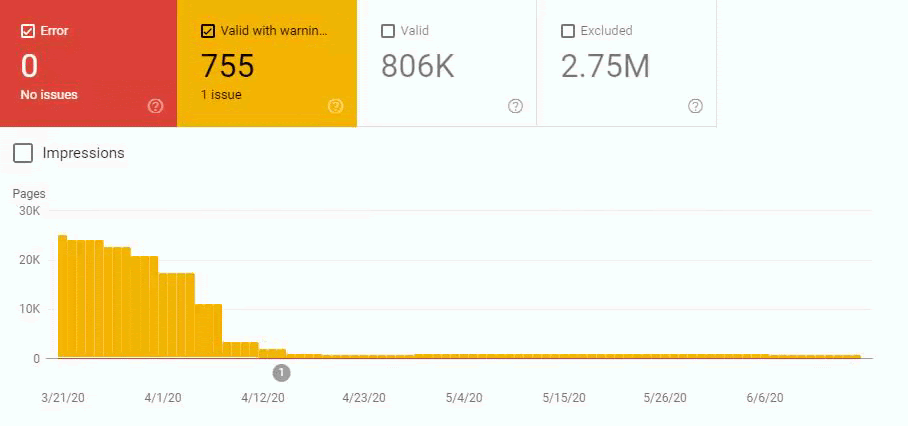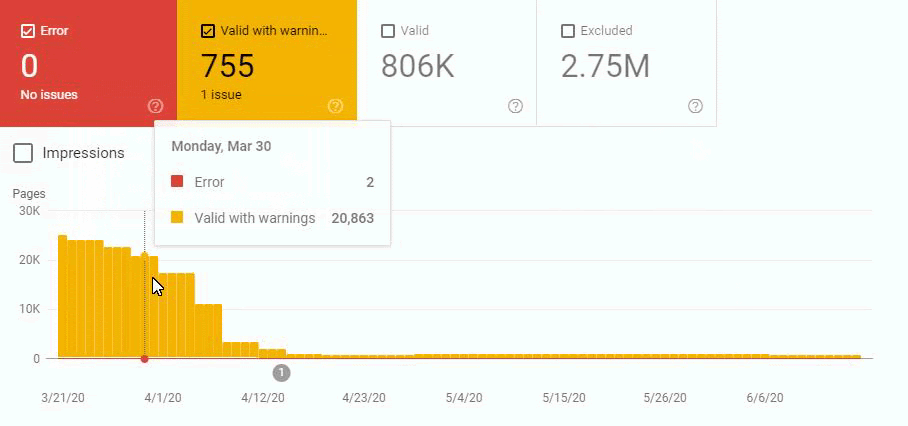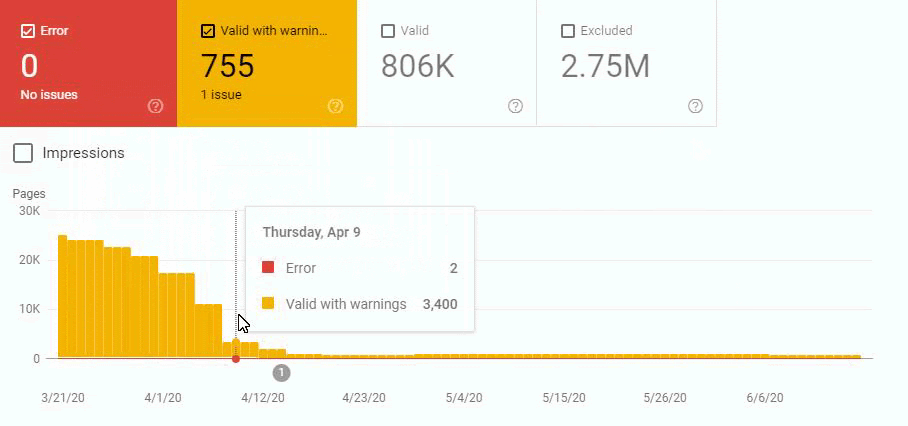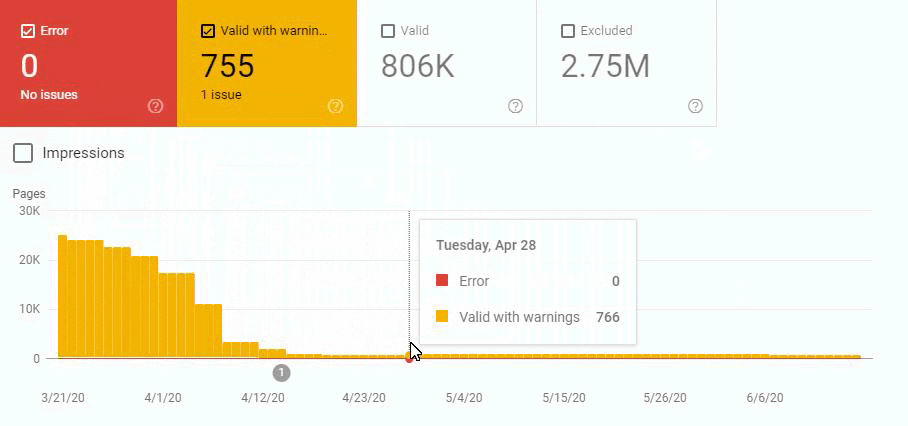
So, we have mixed the second and third methods here. Because of this situation, we have regained the %90 of the Organic Traffic Loss slower. We have lost them in 3 weeks, regained them for 1 month.
Also, Googlebot was crawling more than 15.000 Pages in a day because of this URL bloating. After we fixed that, it continued to crawl 15.000 pages for 1 month. It always seems that there is 404 for the %99 of the time. After a while with the help of 410 Status Codes and its own Algorithms, it started to crawl 10.000 and 5.000 pages in a day.
After a while, it decreased to 300-400 web pages as it should be.
These fluctuations are also reflected in our Coverage Report. In one day we have decreased our Valid and Excluded Web Page amount more than 200.000. But after this, it also increased between 30.000 and 40.000 on different days.
In other words, we didn’t change the URL Amount after our new Deployment for the new URL Structure. But still, in the eyes of Google, our Coverage Report has 200.000 decreases and 30.000 increases. This was also because of the Disambiguation Algorithms and Uncertainty Principles and Algorithm Hierarchies of Search Engines.
An algorithm sees that URL has been deleted but it is not being reflected in the SERP or Index (SERP and Index are not the same things.) Another Algorithm sees that the deleted web page still has internal links and close variations or different canonical tags and puts it back to the coverage report. Another algorithm sees that the web page isn’t on the sitemap and also it gives 404 for the last two weeks and it lost the internal links…
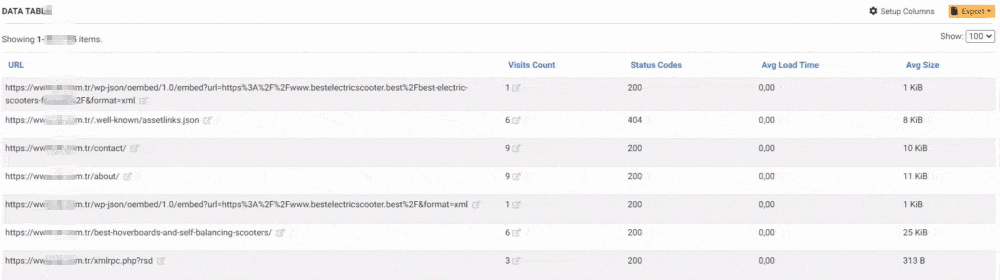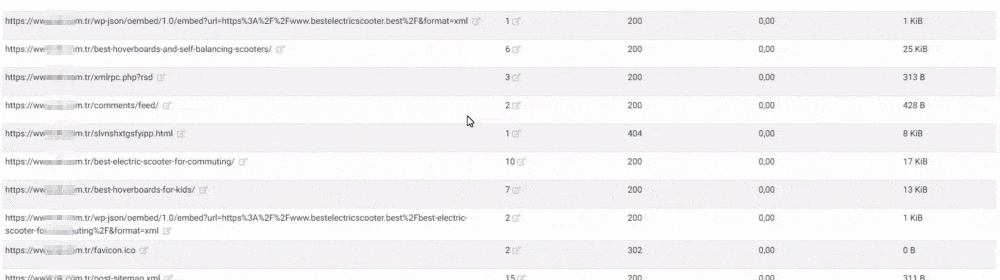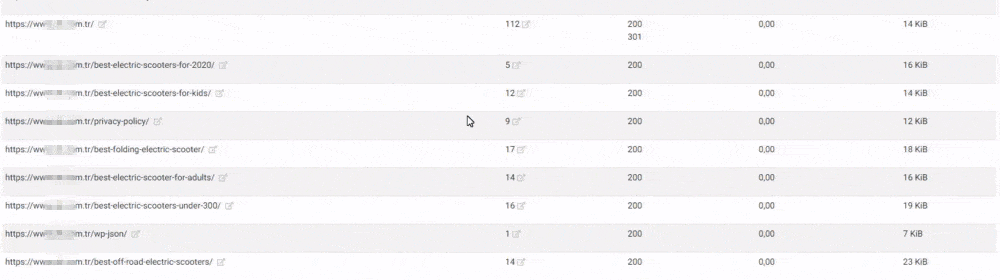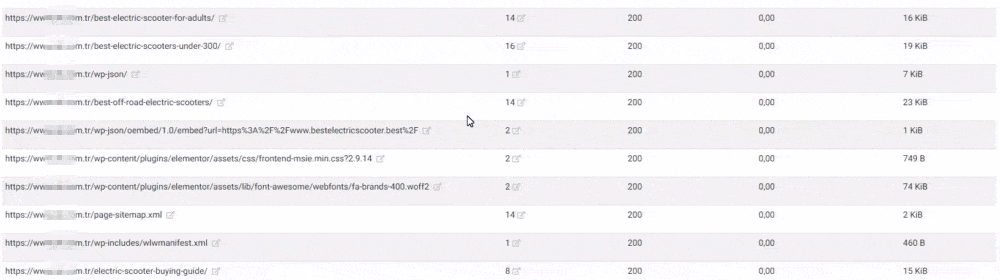
Conclusion of This SEO Case Study
This is a process and that’s why most people always complain about how Crawling, Rendering, and Indexing is slow. If you have a Semantic, Consistent, Stable, and Hierarchical Structure for your Web Entity, you won’t complain in the first place.
You may examine the images which I show for validating these processes. Some of them are not taken at the right time, so you may not see all of the pictures here.
In this SEO Case Study, I could have given you a simple 500 words. (Maybe some of them say, yes, you should do that.) But, I think SEOs of 2020 should focus on two different aspects of Search Engines and Marketing mainly.
- One of them is Coding.
- One of them is Search Engine Theories and Analytical Thinking Skills.
If you have coding capabilities and Analytical Thinking Skills, I think you can go beyond the Traditional SEO and become a Holistic SEO who approaches everything related to SEO from a creative, theoretical, practical, and coding perspective.
I am open to any kind of constructive criticism.
If you have any questions or criticisms, please share them with me.
Lastly, I congratulate JetOctopus on developing one of the deepest perspectives toward SEO and the integration of Data Science and Critical Analysis with SEO in their technology.

